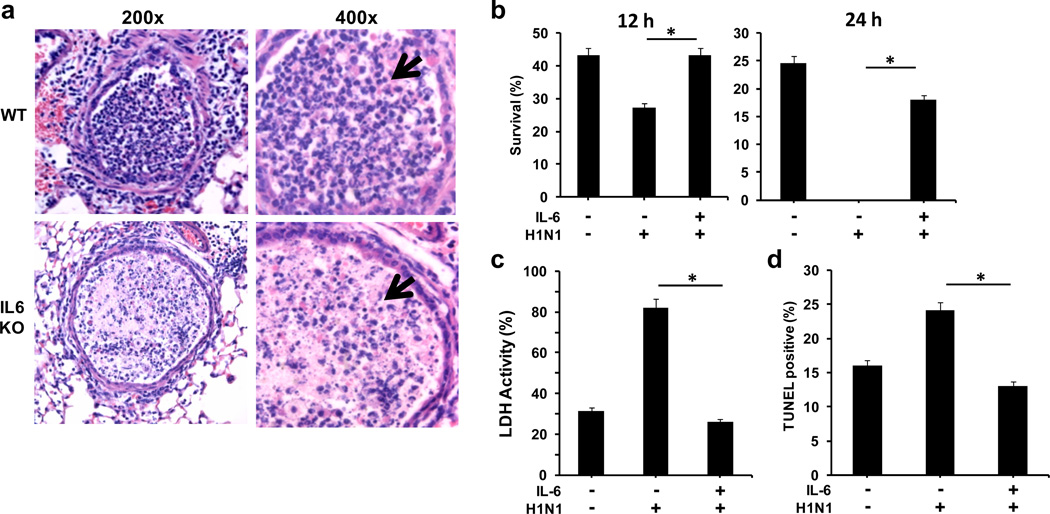
Figure 5. IL-6 protects neutrophils from H1N1 virus-mediated apoptosis.
(a) Histopathology of lungs (H&E staining) from WT and IL-6 KO mice at day 5 p.i. with PR8 H1N1 virus. 200x and 400x magnifications of airways are shown. Arrows point to well-defined polymorphonuclear neutrophil in WT airways, and apoptotic nucleus in IL-6 KO airways. (b) Neutrophils from WT mice were cultured in the presence or absence of PR8 H1N1 virus at 1:10 neutrophil:virus (EIU) ratio with or without IL-6 (20 ng/ml). After 12 h and 24 h, live cells were counted by trypan blue staining. Values (mean +/− SD, n=3) represent the frequency of live cells recovered relative to the initial number. (c) LDH activity in supernatants from neutrophils cultured as described in (b). (d) Neutrophils were cultured as in (b) and apoptosis was determined by TUNEL assay and flow cytometry analysis. Values show the percentage of TUNEL positive cells (mean +/− SD, n=3). * denotes p<0.05. Statistical significance was determined by student’s t test. Results are representative of 2–3 independent experiments.