Fig. 2.
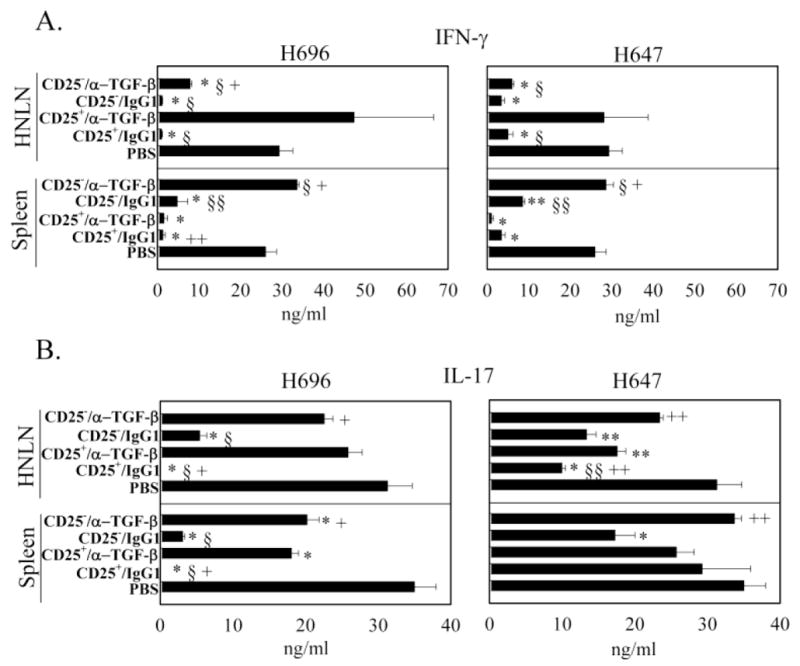
Adoptively transferred Salmonella-CFA/I-induced CD25+CD4+ T cells suppress IFN-γ and IL-17 production. At the peak of EAE, A, B, HNLN (top panels) and splenic (bottom panels) mononuclear cells were PLP139–151-restimulated for 3 days, and A, IFN-γ and B, IL-17 production in culture supernatants were measured by cytokine-specific ELISA. Cytokine production by recipients adoptively transferred with CD4+ T cell subsets from Salmonella-CFA/I (H696; left), and Salmonella vector (H647; right) was measured for the various treatment groups: PBS, CD25+CD4+ T cells plus IgG1, CD25+CD4+ T cells plus anti-TGF-β mAb, CD25− CD4+ T cells plus IgG1, and CD25− CD4+ T cells plus anti-TGF-β mAb. Data depict the mean ± SEM of triplicate wells combined from two experiments: *, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.05 versus PBS; §, p < 0.001; §§, p < 0.05 versus CD25+/α-TGF-β and +, p < 0.001; ++, p < 0.05 versus CD25−/IgG1.
