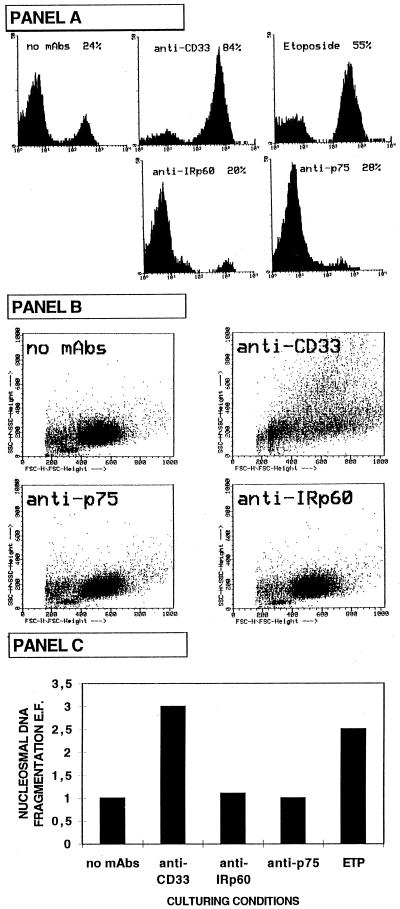
Figure 3.
Anti-CD33 mAb-induced apoptosis in AML cells. (A) The surface binding of Annexin V was measured at different time intervals by flow cytometric analysis. The experiment shown is representative of 10 independent experiments by using the 2412 M5 AML. Leukemic cells were cultured for 40 h with GM-CSF in the presence of anti-CD33 or anti-p75/AIRM-1 or anti-IRp60 mAbs or etoposide (68 μM). Samples were stained with anti-Annexin V FITC-conjugated mAb. Analysis was performed on PI-negative, viable cells. (B) Flow cytometric analysis to evaluate changes in light-scattering properties [forward side scattering (FSC) and side scattering (SSC)] was performed. It is evident that anti-CD33 mAb induced changes in light-scattering properties that are typical of apoptosis (reflecting cell shrinkage and increased granularity). (C) Analysis of DNA fragmentation. Nucleosomal DNA fragmentation has been measured by using an apoptosis-determination ELISA kit (Cell Death Detection ELISAplus; Boehringer Mannheim). The enrichment of mono- and oligonucleosomes released into the cytoplasm has been calculated as absorbance of treated cells/absorbance of untreated cells. The enrichment factor (E.F.) used as a parameter of apoptosis is shown on the y axis as mean of duplicates. Data show the enrichment of nucleosomes in the cytoplasm of cells cultured for 40 h in the presence of GM-CSF (50 ng/ml) under different conditions.