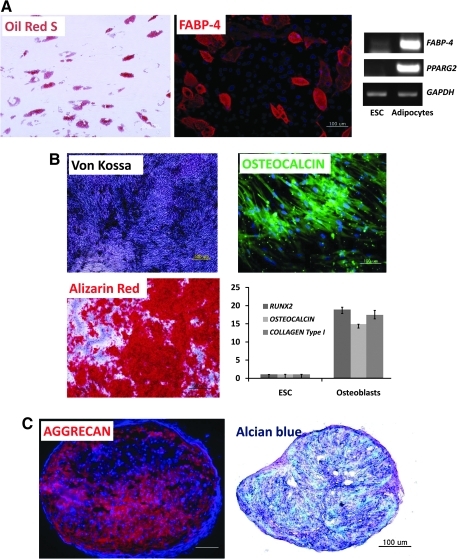
FIG. 4.
Differentiation potential of hESC-derived MSCs. (A) Differentiation of hESC-derived CD105+ cells into adipocytes: Oil-Red S staining and immunostaining with FABP-4 antibody were used to detect lipid drops (red color) and FABP-4 (red color) in adipocytes, respectively. Scale bar is 100 μm. Transcripts of FABP-4 and PPARG2 were detected by RT-PCR. (B) Differentiation of hESC-derived CD105+ cells into osteoblasts; Von Kossa staining (black color) and Alizarin Red staining (red color) were used to detect the calcium deposits in osteoblast cells (scale bar is 500 μm). Osteocalcin, a typical osteoblast marker, was also detected by immunostaining (scale bar is 100 μm). RUNX2, OSTEOCALCIN, and COLLAGEN Type I transcripts were analyzed by real-time PCR. (C) Differentiation of hESC-derived CD105+ cells into chondrocytes; the 5–10-μm pellet sections were stained with Alcian Blue and immunostained with aggrecan antibody to detect glycosaminoglycans (blue color) and aggrecan (red color) in chondrocytes, respectively. Scale bar is 100 μm. RT-PCR, reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction; FABP, fatty acid-binding protein.