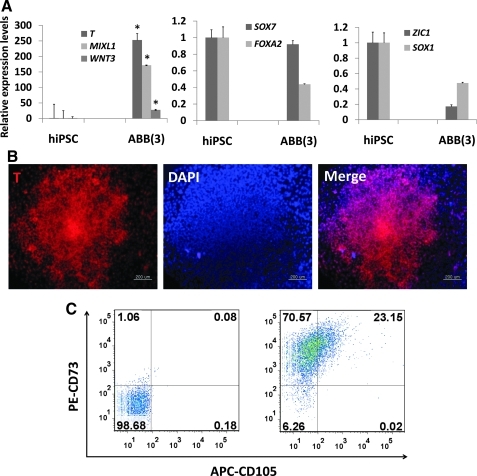
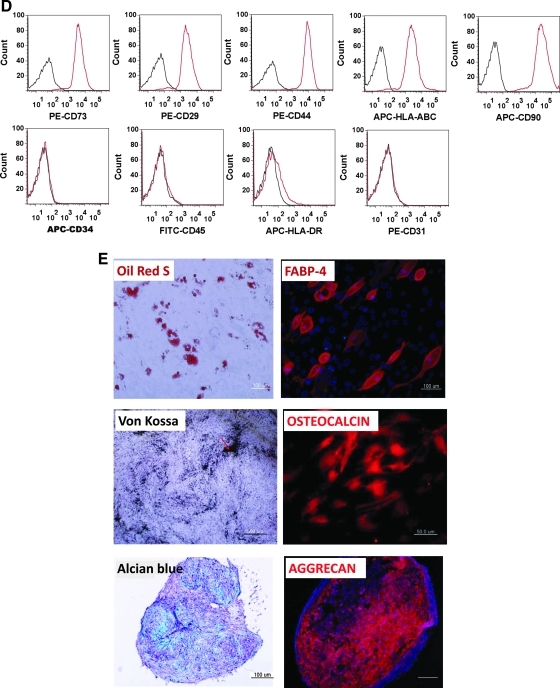
FIG. 5.
Differentiation of hiPSCs into functional CD105+ MSCs. (A) Expression patterns of mesoderm-lineage genes (T, MIXL1, and WNT3), ectoderm-lineage genes (SOX1 and ZIC1), and endoderm-lineage genes (SOX17 and CXCR4) in ABB-treated hiPSCs. Real-time PCR was used to estimate and compare the expression levels of early developmental genes in untreated hiPSCs (control) and ABB-treated hiPSCs. Statistical significance among samples was evaluated by paired t-test (*P<0.05). (B) Protein level expression of the mesoderm-lineage gene T in ABB-treated hiPSCs. Scale bar is 100 μm. (C) Proportion of the CD105+CD73+ cell population after culturing in MSC-induction medium for 10 days. In this figure, PE-CD73 and APC-CD105 were used for FACS and isotope controls (left figure) were used as a negative control. (D) FACS was used to characterize surface-antigen profiles of sorted cells using the following antibodies: PE-CD29, PE-CD44, APC-CD90, PE-CD73, PE-HLA-ABC, PE-CD31, FITC-CD45, APC-HLA-DR, and APC-CD34. (E) Differentiation potentials of hiPSC-derived MSCs. Oil-Red S staining and immunostaining with FABP-4 antibody were used to detect lipid drops (red) and FABP-4 (red) in adipocytes, respectively (top figures). Scale bar is 100 μm. Von Kossa staining and immunostaining with osteocalcin antibody were used to detect calcium deposits (black color; scale bar is 100 μm) and osteocalcin (red color; scale bar is 50 μm) in osteoblasts, respectively (middle figures). Alcian blue staining and immunostaining with aggrecan antibody were used to detect glycosaminoglycan (blue) and aggrecan (red) in chondrocyte pellets, respectively (bottom figures). Scale bar is 100 μm. hiPSCs, human induced pluripotent stem cells; MSC, mesenchymal stem cell; DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (nuclear staining solution).