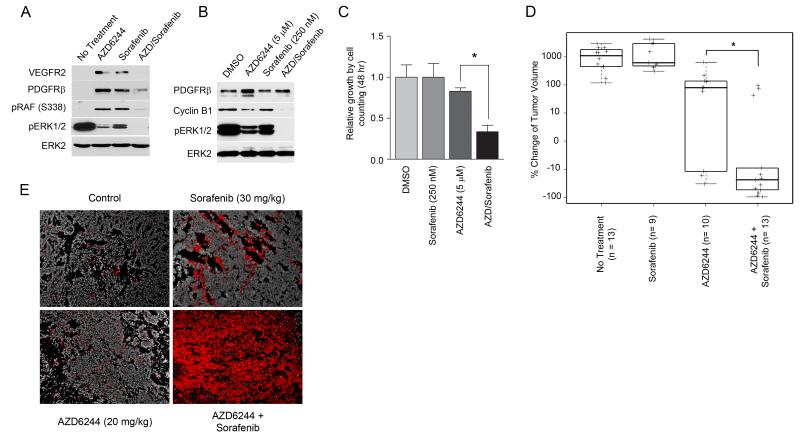
Figure 7. Combination of AZD6244 and sorafenib causes apoptosis and tumor regression in C3Tag TNBC mouse model.
(A) AZD6244 (20 mg/kg) or sorafenib (30 mg/kg) fed in chow results in ERK activation after 2d of treatment in C3Tag GEMM, while cotreatment with AZD6244 and sorafenib inhibits RTK-mediated ERK activation. RTK reprogramming was monitored in tumors treated with AZD6244 and/or sorafenib relative to untreated tumors by western blot.
(B) Sorafenib inhibits AZD6244-dependent reactivation of ERK, promoting c-Myc degradation and loss of cyclin B1 expression in T2-C3Tag cells. T2-C3Tag cells were treated for 24h and analyzed by western blot.
(C) AZD6244 and sorafenib synergize to inhibit cell growth in C3Tag cell line. T2-C3Tag cells were treated with AZD6244 and sorafenib, alone or in combination, and cell growth determined by cell counting (*p-value<0.001; quadruplicate experiments).
(D) Cotreatment of C3Tag mice with AZD6244 and sorafenib for 21d causes significant tumor regression compared to AZD6244 alone. C3Tag mice were treated with AZD6244 (20 mg/kg), sorafenib (30 mg/kg) or the combination of AZD6244 and sorafenib and compared to untreated tumors. Percent change in tumor volume of drug treated relative to untreated is shown (* Wilcoxon p-value=0.007).
(E) Increased apoptosis of C3Tag mouse tumors following cotreatment with AZD6244 and sorafenib. Apoptosis in C3Tag tumors treated for 2d was determined by TUNEL staining (shown in red; DAPI is grayscale).
See also Figure S7.