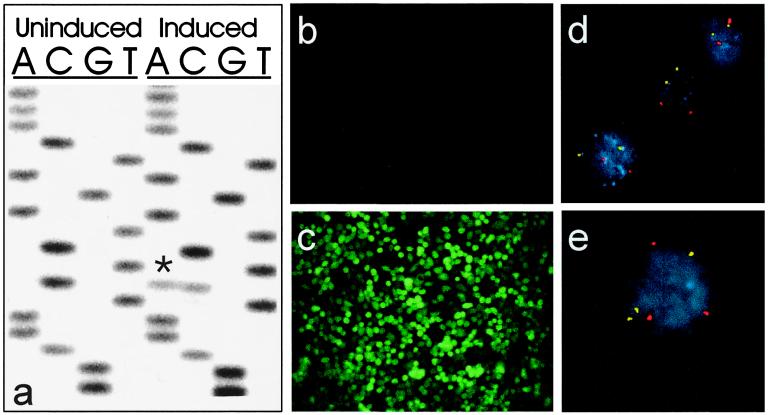
Figure 4.
Inducible expression of a mutant hBUB1 allele confers CIN. (a) Sequence of hBUB1 transcripts assessed by reverse transcription–PCR analysis of RNA from BUB-DLD1 cells. The exogenous mutant hBUB1 gene contained a C-to-A transversion at codon 492 (marked by *), resulting in a substitution of tyrosine for serine. Before induction, there was no mutant hBUB1 transcript detectable, whereas after induction, the level of mutant hBUB1 expression was similar to that of the endogenous wild-type hBUB1 gene. (b) Fluorescence microscopy showed no detectable expression of the coexpressed GFP gene before induction, but (c) uniform expression of GFP after induction. (e) Cells expressing mutant hBUB1 after induction were chromosomally unstable, as indicated by an abnormal number of FISH signals in a high fraction of cells, whereas uninduced cells (d) were stable. The red and yellow dots represent centromeric probes specific for chromosomes 7 and 12, respectively.