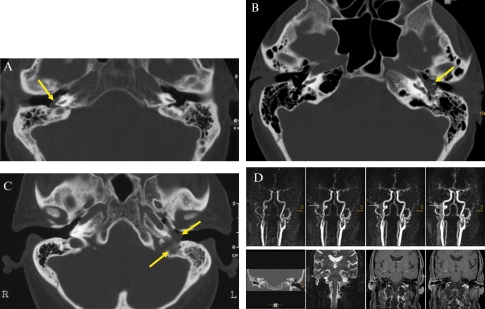
Figure 2.
Fisch classification. The tumors are indicated by yellow arrows. (A) Tympanic paraganglioma (Fisch class A): axial CT scan of a tympanic paraganglioma (bone window) on the right promontory. Note the absence of any bony erosion. (B) Tympanic paraganglioma (Fisch class B): the axial CT scan reveals a left-sided tympanic paraganglioma surrounding and partially destroying the ossicles. The malleus and stapes could not be discriminated. The tumor had also invaded the hypotympanon. There was no destruction of the bone wall to the jugular bulb. (C) Jugular paraganglioma (Fisch class C): axial CT scan showing a left-sided jugular paraganglioma. Note the bone destruction between the jugular bulb and the soft tissue tumor in the hypotympanon. (D) Tympanic paraganglioma (Fisch class D): time-resolved contrast-enhanced MR-angiography (upper row) depicts an early venous drainage attributed to arterio-venous fistulas within this tympanic paraganglioma (solid arrows). Coronal CT (lower row left) of the petrous bone shows a soft tissue tumor with encasement of the ossicles within the whole tympanon, and destruction of the tegmen tympani. Coronal T2-weighted and contrast enhanced T1-weighted images show a small, but distinct, intracranial but extradural tumor growth on the lateral skull base (dotted arrows, lower row).