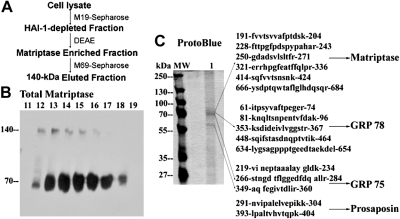
Fig. 7.
The 140-kDa complex is homodimer of activated matriptase. A: purification scheme for the 140-kDa matriptase complex. The 140-kDa matriptase complex was purified from 184 A1N4 lysates through a 3-step purification scheme. Complex preparation was first separated from the 120-kDa HAI-1 complex by HAI-1 M19-Sepharose, followed by DEAE and activated matriptase mAb M69 immunoaffinity chromatography. B: partial purification of 140-kDa matriptase complex by DEAE chromatography. HAI-1-depleted fractions were further purified by DEAE chromatography. Column fractions (11–19) were analyzed using total matriptase mAb M24. Both 140-kDa complex and latent matriptase were eluted in similar fractions 12–18. There was no matriptase-HAI-1 complex in these DEAE fractions. C: immunoaffinity purification and proteomic protein identification of 140-kDa matriptase complex. The 140-kDa matriptase complex-enriched DEAE fractions (from Fig. 7B) were then purified by immunoaffinity chromatography with activated matriptase mAb 69. Eluted proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE under nonreducing and nonboiled condition and the gel stained with ProtoBlue (lane 1). The 70-kDa matriptase dissociated from the 140-kDa matriptase complex eluted as major proteins from immunoaffinity column and one 60-kDa minor protein was also seen in eluted fractions. Protein molecular weight markers (MW) are indicated. Proteomic protein identification of the subunits of the 140-kDa matriptase complex revealed that there were 14 tryptic fragments derived from the 70-kDa protein spots matched to 6 stretches of amino acid sequences of matriptase; 5 fragments matched to 5 stretches of amino acid sequences of GRP 78 and 3 fragments matched to 3 stretches of amino acid sequences of GRP 75. The 60-kDa spots yielded 2 fragments matched to 2 stretches of amino acid sequences of prosaposin. These tryptic fragments were presented by their amino acid sequences.