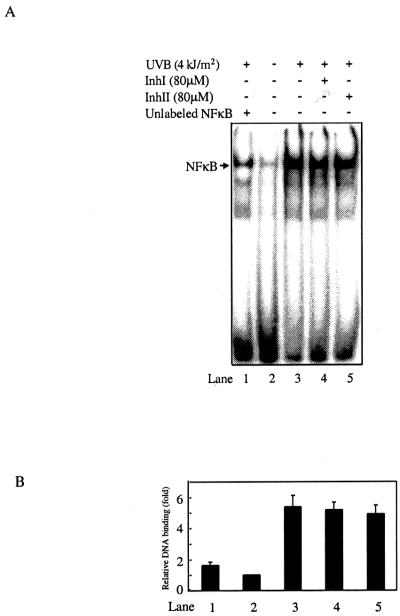
Figure 4.
Inh I and Inh II do not affect UVB-induced NFκB DNA binding. JB6 Cl 41 cells were treated, nuclear proteins were extracted, and electrophoretic mobility-shift assays were carried out as described in the text. (A) UVB strongly induces NFκB DNA binding (lane 3), and the binding is specific as indicated by the effective competition of a 10-fold excess of the unlabeled NFκB probe (lane 1). Inh I or Inh II has little effect on UVB-induced NFκB DNA binding (lanes 4 and 5). (B) Densitometry analysis of A from three independent experiments.