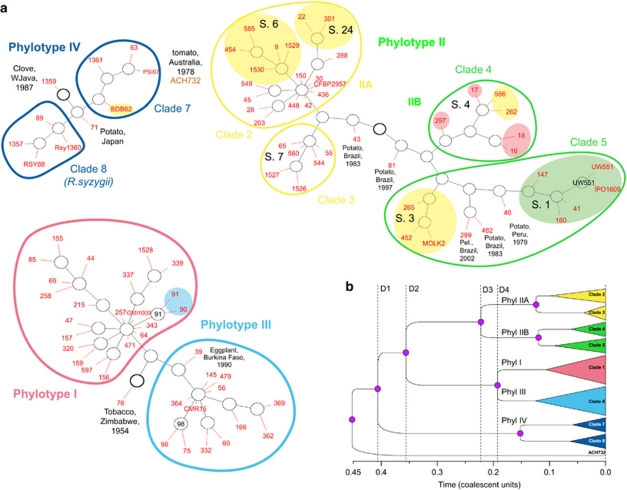
Figure 4.
Gene genealogies of the phylotypes and clades of Ralstonia solanacearum. (a) GraphViz network generated by ClonalFrame. Ancestral nodes inferred are marked in black, and the location of isolates in red, with each red line representing a single isolate. The ancestral node of each network component is indicated by a thicker circle (Didelot and Falush, 2007). Strains are identified by their RUN ID (see Supplementary Table S1). Yellow shades indicate banana-affecting ecotypes: Moko disease-inducing strains (IIA/sequevars 6 and 24, IIB/sequevars 3 and 4) and BDB (IV/sequevar 10); green shade indicates the ‘Brown Rot' strains (IIB/sequevar 1, formerly race 3/biovar 2), which are preferentially pathogenic to potato and tomato, and are specifically able of inducing disease at cool temperatures (Milling et al., 2009). Red shade indicates ‘emerging' strains that are pathogenic to Araceae, Solanaceae, Cucurbitaceae while not pathogenic to dessert banana (Wicker et al., 2007). Blue shade indicates mulberry-affecting strains (race 5/biovar 5). S., egl-based sequevars (Fegan and Prior, 2005). Outliers (1359 and 71 in phylotype IV; 43, 81, 299, 482 and 40 in phylotype II; 76 and 39 in phylotypes I and III) are identified by their RUN number, with their host, country and year of isolation. Pel., Pelargonium sp. (b) Schematic representation of the majority-rule tree based on the posterior distribution of genealogies inferred by ClonalFrame. D1, divergence of phylotypes IV and I/II/III; D2, divergence of phylotypes II and I/III; D3, divergence of IIA and IIB; D4, divergence of phylotypes I and III.