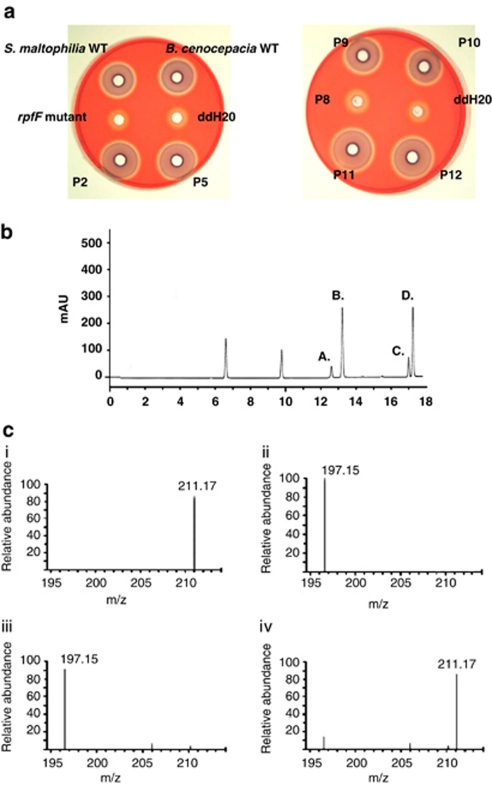
Figure 1.
Detection of DSF-like signal molecules in the sputum of CF patients. (a) Biossay for DSF activity in extracts from sputum of CF patients (designated ‘P' followed by the sample number, that is, ‘P2') or in culture supernatants of wild-type strains of S. maltophilia or B. cenocepacia. The bioassay depends upon the restoration of endoglucanase activity to an rpfF mutant (DSF minus) strain of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. DSF activity was detected in culture supernatants (as expected) and in some of the sputum samples. Endoglucanase activity in the rpfF mutant and negative control (ddH20) are also shown. (b). A representative high-performance liquid chromatography trace showing analysis of DSF extracts from the CF patient sputum. The compounds in fractions a, b, c and d showed strong activity in the DSF bioassay (c). Identification of DSF and BDSF in sputum from CF patients by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. The figure shows MS profiles for (i) synthetic DSF, (ii) synthetic BDSF, (iii) the compound in fraction d identified as DSF and (iv) the compound in fraction c identified as BDSF. The m/z of DSF is 211.17 and BDSF is 197.15.