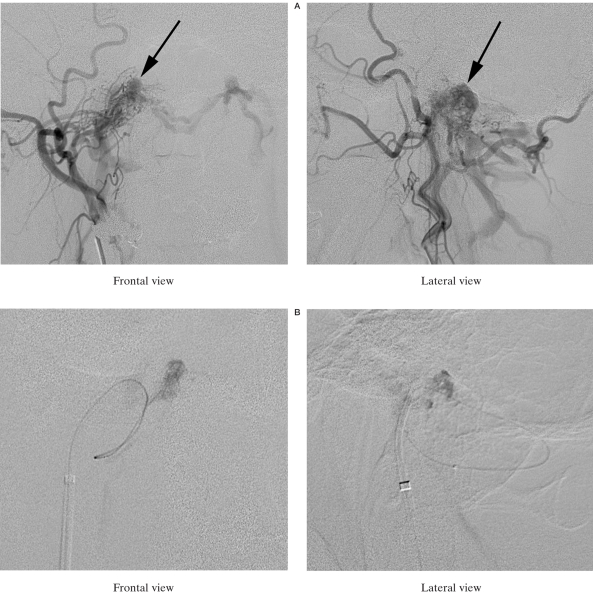
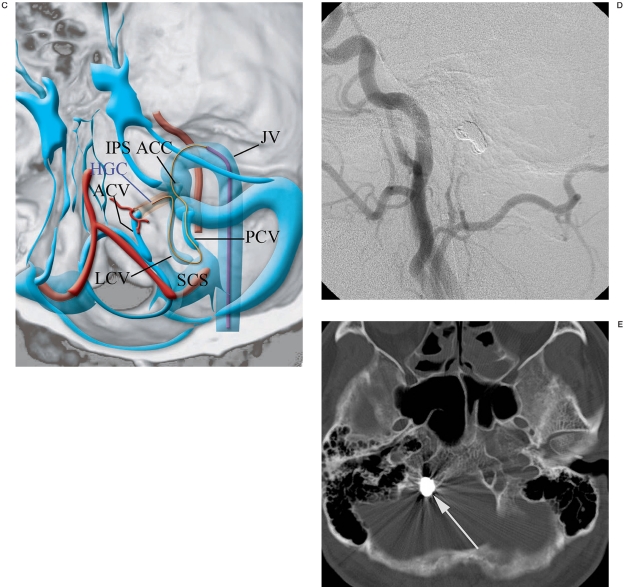
Figure 2.
A) Right external carotid angiography shows DAVF (arrows) fed by the ascending pharyngeal artery and occipital artery. This DAVF drained into the suboccipital cavernous sinus and contralateral condylar veins via the lateral and posterior condylar veins. B) The microcatheter was introduced into the anterior condylar vein via the sigmoid sinus, posterior condylar vein, suboccipital cavernous sinus and lateral condylar vein. C) Schematic drawing of the catheterization route from the sigmoid sinus to the anterior condylar vein. IPS: inferior petrosal sinus, ACC: anterior condylar confluence, ACV: anterior condylar vein, PCV: posterior condylar vein, LCV: lateral condylar vein, SCS: suboccipital cavernous sinus, HGC: hypoglossal canal, JV: jugular vein. D) Right external carotid arteriogram shows complete disappearance of DAVF. E) CT shows coils located in the right hypoglossal canal (arrow).