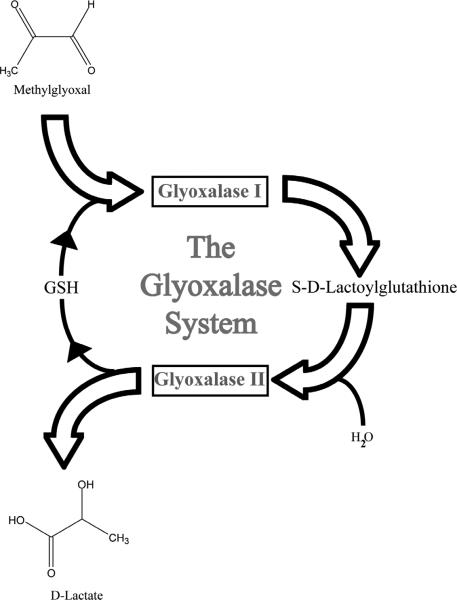
Figure 2.
The glyoxalase system is composed of two enzymes, glyoxalase I (GLO1) and glyoxalase II. Reactive dicarbonyls, like methylglyoxal, are effectively detoxified via this metabolic pathway. The glyoxalase enzyme pathway catalyzes the conversion of reactive α-oxoaldehydes into the corresponding α-hydroxyacids. In this schematic, methylglyoxal reacts with glutathione and is converted to S-d-Lactoylglutathione by GLO1. This intermediate is then broken down into d-lactate by glyoxalase II and reduced glutathione is recycled.