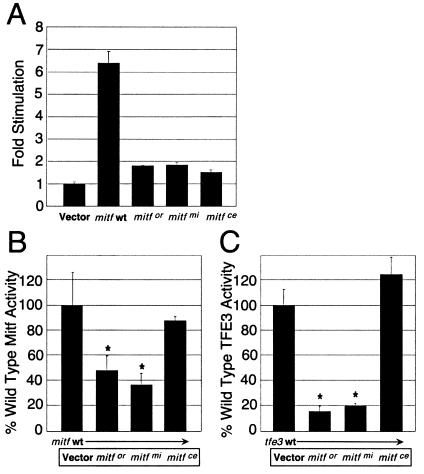
Figure 5.
(A) The wild-type (wt) Mitf protein up-regulates the human cathepsin K promoter whereas Mitfmi, Mitfor, or Mitfce mutant proteins have no significant transactivation activity. The wild-type human cathepsin K promoter −928 bp to +2 luciferase reporter was transfected into MCF-7 cells in the presence of wild-type Mitf, Mitfor, Mitfmi, Mitfce, or a vector control. The transfections were performed in triplicate with bars indicating standard errors. (B and C) Mitf mutants, Mitfor, and Mitfmi, which cause osteopetrosis in animal models, decrease the ability of wild-type Mitf (B) and TFE3 (C) to transactivate the cathepsin K promoter. The wild-type human cathepsin K promoter −928 bp to +2 luciferase reporter was transfected into MCF-7 cells in the presence of wild-type Mitf (B) or TFE3 (C) plus mutant Mitf (Mitfor, Mitfmi, or Mitfce), or vector controls. The transfections were performed in triplicate with bars indicating standard errors. The data are presented as % wild-type Mitf or TFE3 activity on the human cathepsin K promoter after subtracting vector only control. * indicates statistically significant repression of wild-type Mitf or TFE3 function by mutant Mitfor and Mitfmi (P < 0.04), whereas the nonosteopetrotic allele Mitfce did not affect wild-type Mitf and TFE3 activities.