Table 1. Overview of networks used in our analysis.
| network type |
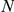
|
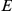
|
density | GCC |
| Arabidopsis thaliana (BG) | 1675 | 2953 | 0.00210 | 1212 |
| Homo sapiens (BG) | 8429 | 29321 | 0.00082 | 8114 |
| Mus musculus (BG) | 545 | 490 | 0.00330 | 141 |
| Drosophila melanogaster (BG) | 7034 | 22222 | 0.00089 | 6907 |
| Caenorhabditis elegans (BG) | 2806 | 4457 | 0.00113 | 2575 |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae (BG) | 5620 | 53309 | 0.00337 | 5611 |
| Schizosaccharomyces pombe (BG) | 1411 | 2478 | 0.00249 | 1313 |
| Escherichia coli (DIP) | 2856 | 6712 | 0.00164 | 2159 |
| Helicobacter pylori (DIP) | 1066 | 1415 | 0.00249 | 976 |
| Mycoplasma pneumoniae (IA) | 415 | 735 | 0.00855 | 375 |
| Rattus norvegicus (IA) | 1232 | 1421 | 0.00187 | 1095 |
| Western States Power Grid | 4941 | 6594 | 0.00054 | 4941 |
| Coauthorship Netscience | 1589 | 2742 | 0.00217 | 379 |
| Collaboration Hep-th | 8361 | 15751 | 0.00045 | 5835 |
The first 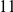 networks are protein networks and the bottom
networks are protein networks and the bottom  are technological and social networks. The columns refer to the number of nodes (
are technological and social networks. The columns refer to the number of nodes (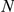 ) and edges (
) and edges (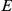 ) in the network, density is the edge density and GCC is the giant connected component. BG: BioGrid database, IA: IntAct database.
) in the network, density is the edge density and GCC is the giant connected component. BG: BioGrid database, IA: IntAct database.
