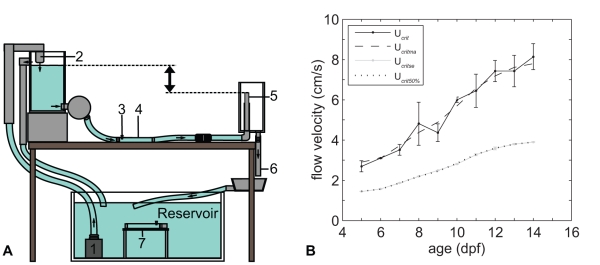
Figure 6. Schematic representation of the swim-training set-up in lateral view and critical flow velocity.
A) Water was pumped (1) to the top aquarium and flowed back into the reservoir via the training tubes (4), outflow tubes (5) and outflow hoses (6) due to gravity. The difference in water level between the top aquarium and the outflow tubes (5) (indicated with up down black arrow) determined the flow velocity in the training tubes (4). Control fish were kept in similar tubes in the same set-up (7). Both the training and control section consisted of five tubes placed parallel to each other (not visible in drawing). Each tube had its own outflow tube and hose. B) Critical flow velocity (Ucrit) over time and during swim-training experiments (Ucritse). Zebrafish were subjected to 50% (Ucrit 50%) of the moving average Ucrit (Ucritma).