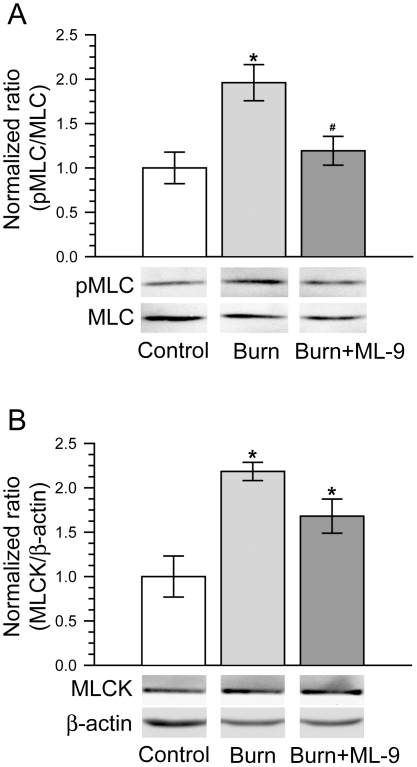
Figure 6. MLCK inhibition with ML-9 abolishes the increase of MLC phosphorylation after burn injury.
A. Both phosphorylated MLC and total MLC in ileal mucosa were determined by Western blot at 6 hours after 30% TBSA burn. MLC phosphorylation was significantly increased following burn injury. MLCK inhibition with ML-9 abolishes the burn-caused increase of MLC phosphorylation. Data are representative of five similar experiments. *p<0.05 compared with control. #p<0.05 compared with burn. B. MLCK protein expression in ileal mucosa was analyzed by Western blot at 6 hours after 30% TBSA burn. Burn injury induced a significant increase of MLCK protein expression. ML-9 treatment had no significantly effect on the burn-induced increase of MLCK protein expression. Data are representative of five similar experiments. *p<0.05 compared with control.