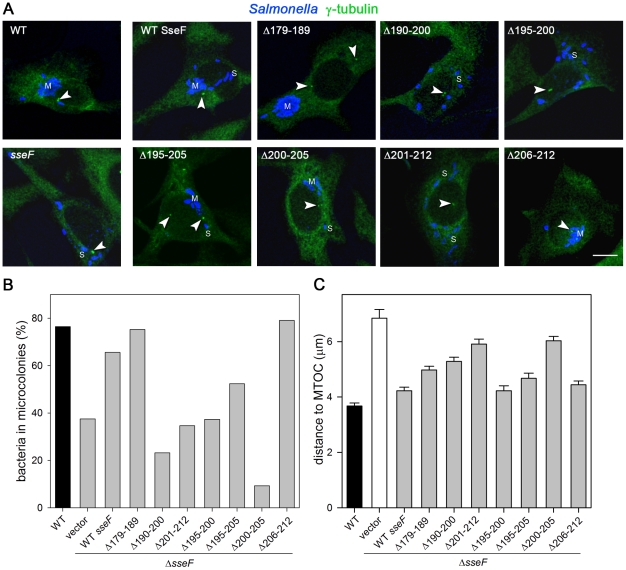
Figure 2. Role of the C-terminal hydrophobic domain in SseF for positioning of Salmonella-containing vacuoles in infected cells.
HeLa cells were infected with Salmonella WT, the sseF-deficient strain or the sseF-deficient strain harboring plasmids for the expression of WT sseF or various mutant alleles. Cells were fixed with MeOH 16 h after infection and subjected to immuno-staining for the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) using γ-tubulin antisera (detected with α mouse Alexa488, green), and for Salmonella using α O-antigen antisera (detected with α rabbit Alexa647). A) Representative infected cells are shown and arrowheads indicate the location of MTOC. In cells with multiple MTOC, the distance of the SCV to the proximal MTOC was determined. Microcolonies were defined as clusters of at least 5 bacteria in close proximity and examples are indicated by M. Scattered SCV are indicated by S. Scale bars, 20 µm. B) Intracellular Salmonella were scored for location in microcolonies or scattered SCV. At least 25 infected cells of approximately uniform size were identified, images were acquired using Leica SP5 CLSM and the percentage of bacteria in microcolonies was calculated. C) The distance between individual intracellular bacteria and the MTOC was determined using ImageJ software. Means and standard errors of mean for 250 to 600 intracellular bacteria per strains are shown and the data are representative for two independent experiments.