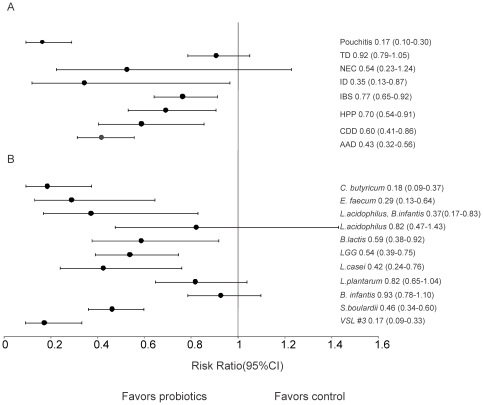
Figure 3. The effect size (risk ratio) for gastrointenstinal diseases and for probiotic species.
(A) The effect size including the 95% confidence intervals for the total events of Antibiotic associated diarrhea (AAD), Clostridium difficile disease (CDD), Helicobacter pylori positive (HPP), Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Infectious diarrhea (ID), Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NE), Traveller's diarrhea (TD), and Pouchitis during which probiotics were taken. (B) The effect size including 95% confidence intervals for the type of probiotic species that were used to treat and prevent gastrointestinal disease. The species that were used were VSL#3, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG), Saccromyces boulardii, Bifidobacterium infantis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei, Clostridium butyricum, Enterococcus faecum, Lactobacillus plantarium, Bifidobacterium lactis and Lactobacillus acidophilus combined with Bifidobacterium infantis. Risk ratios below one favor the probiotic while risk ratios above one favor the placebo.