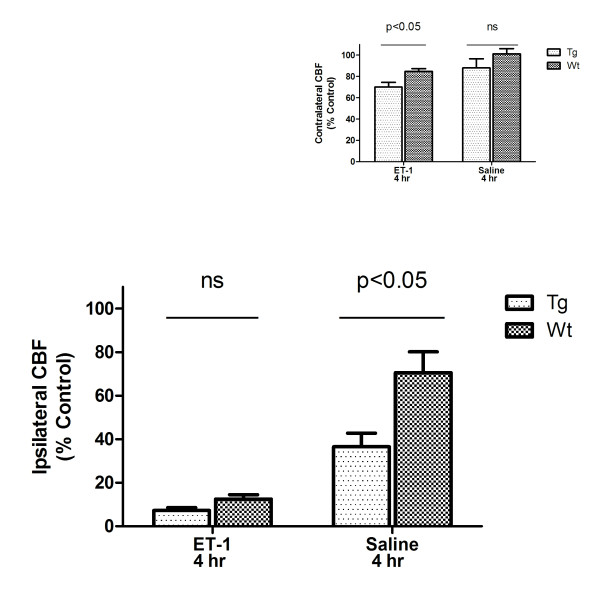
Figure 2.
Cerebral blood flow (CBF) is decreased 4 hours after intra-cortical injection of endothelin-1 (ET-1) or saline. CBF was quantitated, relative to pre-injection set at 100%, in a 0.9 cm diameter circular region-of-interest centered on the injection site. Two-way ANOVA of ipsilateral CBF indicated a significant effect of genotype (F(1, 29) = 27.4, p < 0.01), a significant drug effect (F(1, 29) = 136.1, p < 0.001) and a significant genotype by drug interaction (F(1, 29) = 14.8, p < 0.01). Bonferroni post-tests indicated a significant difference (p < 0.05) between Wt and Tg mice injected with saline but not between Wt and Tg mice injected with ET-1. Inset ET-1, but not saline, injections were associated with decreased contralateral CBF. Two-way ANOVA of contralateral CBF at 4 hours also indicated a significant effect of genotype (F(1, 29) = 7.01, p < 0.05) and a significant drug effect (F(1, 29) = 10.6, p < 0.01). Bonferroni post-tests indicated that ET-1 produced a significantly greater decrease in contralateral CBF in Tg mice than in Wt littermates (p < 0.05). Data are means ± SEM, n = 12 Tg ET-1, 13 Wt ET-1, 4 Tg saline and 4 Wt saline.