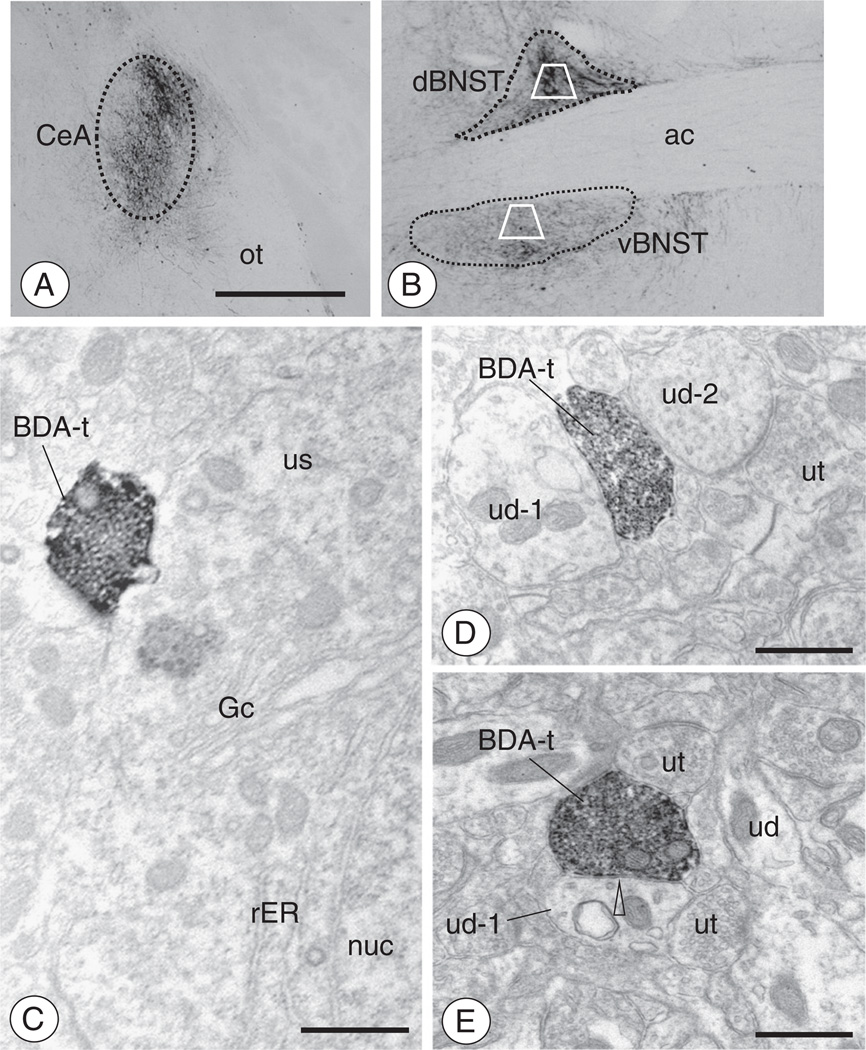
Fig. 7.
Administration of BDA in the CeA results in anterogradely labeled axonal processes and boutons in the BNST(A–B). As shown by light microscopy, administration of BDA into the CeA resulted in anterograde transport in the BNST. Fibers and punctate granules resembling boutons were present throughout the ventral and dorsal BNST. Areas bound by trapezoids represent regions of the dorsal and ventral BNST sampled by electron microscopy. (C). Electron micrograph showing a BDA labeled axon terminal (BDA-t) contacting the cell body of a dBNST neuron (us). Both Golgi (Gc) and rough endoplasmic reticula (rER) are seen near the nucleus (nuc) of this unlabeled soma. (D). An anterogradely labeled axon terminal (BDA-t) contacts a dendritic profile (ud-1). An unlabeled axon terminal (ut) and dendritic profile (ud-2) are also seen in the adjacent neuropil. (E). A BDA labeled axon terminal (BDA-t) is present in the neuropil with unlabeled dendrites (ud) and axon terminals (ut). The BDA labeled terminal forms an apparent symmetric inhibitory-type type synapse (open arrow head) with one of the dendritic profiles (ud-1). Scale Bars: (Top) 1 mm; (Bottom) 0.5 µm.