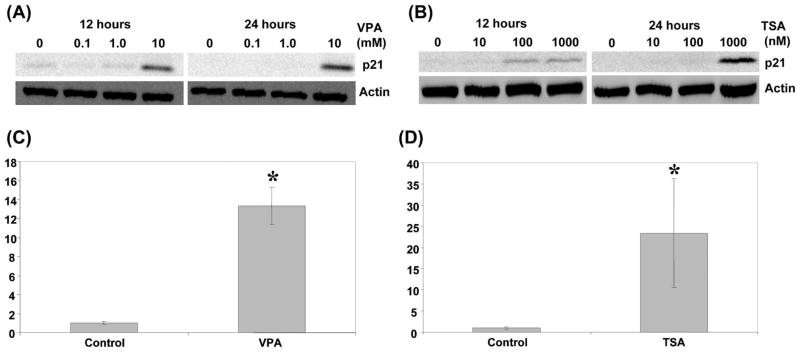
Figure 5.
Effect of TSA and valproic acid on p21 expression. (A) Western blot assay was performed after 12 or 24 h valproic acid treatments at the indicated concentrations. The blot with anti-p21 antibody is shown at the top. β-actin used as a loading control is shown at the bottom. (B) Western blot assay was performed after 12 or 24 h TSA treatments at the indicated concentrations. The blot with anti-p21 antibody is shown at the top. β-actin used as a loading control is shown at the bottom. (C) The relative expression level of p21 mRNA was determined with quantitative RT-PCR after 24 h treatment with 10 mM valproic acid. (D) The relative expression level of p21 mRNA was determined with quantitative RT-PCR after 24 h treatment with 1 μM TSA. In both cases, GAPDH was used to normalize samples. The results represent fold activation over control of three independent experiments with standard deviations. *P<0.05