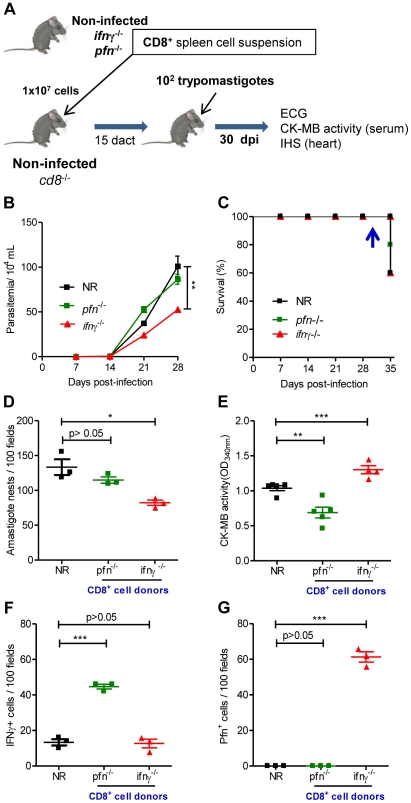
Figure 7. Distinct migratory behavior and effector function of CD8+IFNγ+ and CD8+Pfn+ T-cells in T. cruzi infection.
(A) Experimental scheme of CD8+ cell isolation from noninfected naïve ifnγ −/− pfn +/+ and ifnγ +/+ pfn −/− donors, in vivo reconstitution of the CD8+ cell compartment of naïve cd8 −/− mice, infection with 100 bt of the Colombian strain at 15 days after cell transfer (dact) and analysis at 30 days post-infection. Parasitemia, survival rate, cardiac parasitism and CK-MB activity levels in the serum and colonization of the cardiac tissue by IFNγ+ and Pfn+ cells were evaluated. (B) Parasitemia and (C) survival curve of cd8 −/− mice non-reconstituted (NR) or reconstituted with CD8+ cells from ifnγ +/+ pfn −/− and ifnγ −/− pfn +/+ donors. In independent experiments, the animals were analyzed at 30 dpi when 100% of the mice in all the experimental groups were alive (arrow). (D) Number of amastigote nests in 100 microscopic fields of cardiac tissue sections. (E) Cardiomyocyte lesion evaluated by CK-MB activity in serum samples. The number of (F) IFNγ+ and (G) Pfn+ cells in 100 microscopic fields of cardiac tissue sections from mice non-reconstituted (NR) or reconstituted with CD8+ cells from ifnγ +/+ pfn −/− and ifnγ −/− pfn +/+ donors, at 30 dpi. Each symbol represents an individual mouse. These data represent three independent experiments. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; and ***, p<0.001, comparing cd8 −/− infected mice non-reconstituted and reconstituted with CD8+ cells from ifnγ −/− pfn +/+ and ifnγ +/+ pfn −/− donors.