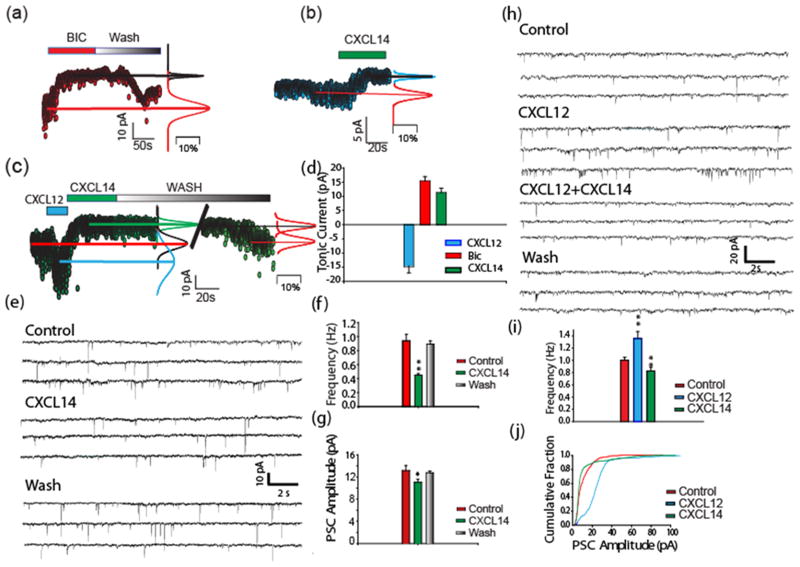
Fig. 3. CXCL14 inhibits GABAergic transmission in the dentate gyrus stem cell niche.
Recordings taken from nestin-EGFP-expressing cells in acutely isolated slices from mouse DG are shown. a): Bicuculline (Bic; 100 μM) and b) CXCL14 inhibited GABAergic PSCs and inhibited the GABAergic tonic inward current in (n=55 and n=7 respectively) c: The enhanced GABAergic current produced by CXCL12 (Bhattacharrya et al 2008)was also inhibited by CXCL14 (10 nM) (n=7). d: Tonic currents produced by CXCL12 (40 nM), CXCL14 (10 nM) and Bicuculline (Bic; 100 μM). e: PSCs recorded from a type 2 nestin-EGFP cell in the absence and presence of CXCL14 (10nM). f, g: PSC frequency and amplitude were significantly decreased in presence of CXCL14 (10 nM) (**p<0.001 and *p<0.04 respectively, n=16). h–j: CXCL14 produced a significant decrease in PSC frequencies and amplitude in the presence of CXCL12. Frequency and amplitude of PSCs recorded from nestin-EGFPcells in presence of CXCL12 (40 nM) and CXCL14 (10 nM). A significant increase in PSC frequency (**p<001) was observed in presence of CXCL12 (40 nM), which was significantly decreased in presence of CXCL14 (10 nM) (**p<0.05,n=9) (i). Increased PSC amplitudes in presence of CXCL12 (40 nM) were significantly decreased (p<0.001) by CXCL14 (10 nM) (n=9) (j). Error bars indicate SEM.