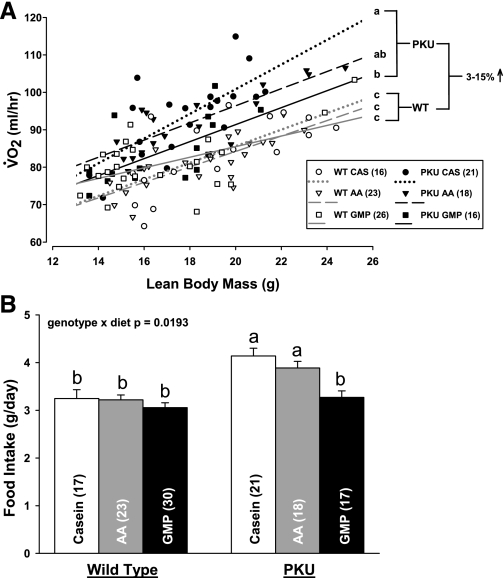
Fig. 3.
Oxygen consumption (V̇o2; A) and food intake (B) in PKU and WT mice fed CAS, AA, and GMP diets. V̇o2 was assessed at 23 wk of age over a 48-h period and analyzed with lean body mass as a covariate. Mean V̇o2 showed a significant effect of genotype (P < 0.0001) and significant interaction of genotype and diet (P = 0.0180) at the mean of lean body mass. Energy expenditure as reflected in V̇o2 was significantly increased by 3–15% in PKU mice compared with WT mice (2.55% increase bGMP; 12.88% increase a,bAA, and 14.82% increase aCAS). a,bDifferent superscripted letters indicate significant differences in mean V̇o2 and food intake based on significant genotype × diet interaction. Male mice consumed significantly more food than female mice without diet interaction (P = 0.04). Values are means + SE; nos. in parentheses indicate sample size.