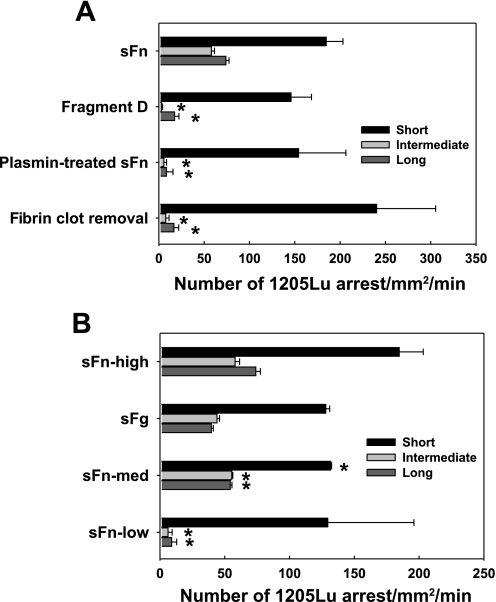
Fig. 2.
sFn-mediated melanoma adhesion to EC is dependent on a divalent binding mechanism. A: fibrin(ogen) fragment D, which contains a half of α, β, and γ chains, plasmin-digested sFn, and residual proteins after fibrin polymer removal, failed to mediate 1205Lu intermediate and long-term adhesion to EC, although still supporting short-term adhesion. B: thrombin and fibrinogen concentrations affect melanoma adhesion. sFn-high, sFn-med, and sFn-low were made, respectively, from 1.5 mg/ml sFg + 2 U/ml thrombin; 1.5 mg/ml sFg + 0.053 U/ml thrombin; and 0.015 mg/ml sFg + 2 U /ml thrombin. sFg was 1.5 mg/ml sFg without adding thrombin. *P < 0.05 compared with the case sFn (A) or sFn-high (B), respectively, in the same arrest duration. Values are means ± SE for n ≥ 3.