Fig. 1.
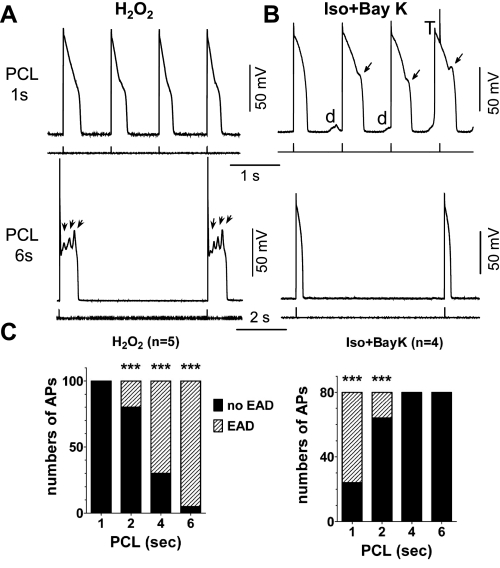
Pacing cycle length (PCL) dependence of early afterdepolarization (EAD) induction in different models. A: action potentials (APs) recorded from rabbit ventricular myocytes treated with 200 μM H2O2 (for 8 min in this case). Representative APs at PCL of 1 s (top) and 6 s (bottom) are shown. EADs were observed at long PCL of 6 s (arrows) but not at PCL of 1 s. B: APs recorded from myocytes treated with 100 nM isoproterenol and 50 nM BayK 8644 (Iso + BayK). EADs (arrows), delayed afterdepolarizations (DADs; d), and triggered AP (T) were induced at PCL of 1 s (top) but not at PCL of 6 s (bottom). C: summarized bar graphs showing the incidence of EADs within 20 APs at various PCLs in the 2 models (n ≥ 4 cells). The EAD incidence rate was higher at a low pacing rate (or long PCL) in the H2O2 model but at fast pacing rate (or short PCL) in Iso + BayK model. ***P < 0.0001, Fisher's exact test vs. no incidence of EADs.