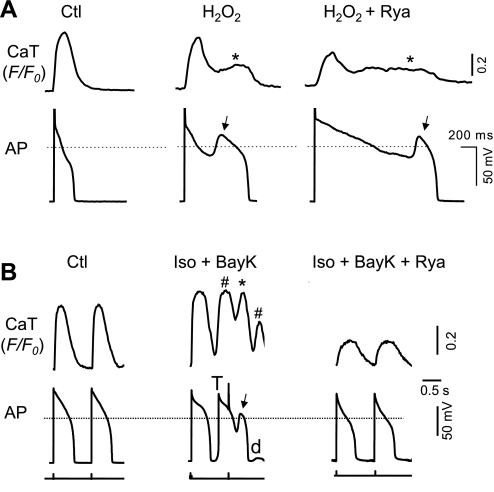
Fig. 7.
Effects of ryanodine (10 μM), a ryanodine receptor inhibitor, on EADs and corresponding SCaTs/CaWs. A: CaT and AP recording under control condition (left), after H2O2 treatment (middle) and the effect of ryanodine (Rya) on H2O2-induced EADs (arrows) and CaTs (*; right). B: CaT and AP recording under control condition (left), after Iso + BayK treatment (middle), and the effect of ryanodine (right). Iso + BayK-induced CaWs (* and #, corresponding to EAD and DAD, respectively), EADs (arrows), and DAD-triggered action potential (T) are indicated.