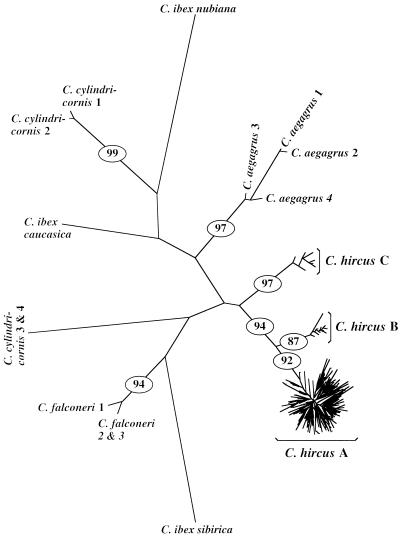
Figure 1.
Neighbor-joining tree of mtDNA types from 406 domestic goats and 14 wild Capra. Trees constructed by using other methods (e.g., UPGMA or neighbor-joining with alpha = 0.20–0.40) were nearly identical in shape. The large star-shaped cluster (C. hircus A) contains 316 mtDNA types (found in 370 individuals and in all breeds). The two smaller lineages (C. hircus B and C) contain only eight and seven mtDNA types (found in 25 and 11 individuals, respectively). C. hircus B was detected only in eastern and southern Asia. C. hircus C was found in Mongolia, Switzerland, and Slovenia (Fig. 2). Numbers on branches are the percent of 2,000 bootstrap trees with the same branch structure. Only bootstrap values >70 are given. The wild taxon with sequences most similar to domestic goats is Capra aegagrus (61.3 substitutions, on average, using the gamma-corrected distance). The second most similar taxon is Capra cylindricornis (84.5 substitutions; see Table 4, which is published as supplemental data on the PNAS web site, www.pnas.org). It is not surprising that some wild taxa appear to be paraphyletic because (i) the taxonomy of Capra is very poorly understood and erroneous taxonomic classifications are possible (7), (ii) paraphyly has been reported (33, 34), and (iii) intertaxon hybridization is possible (23) and is thought to occur in Daghestan where our (paraphyletic) samples originated.