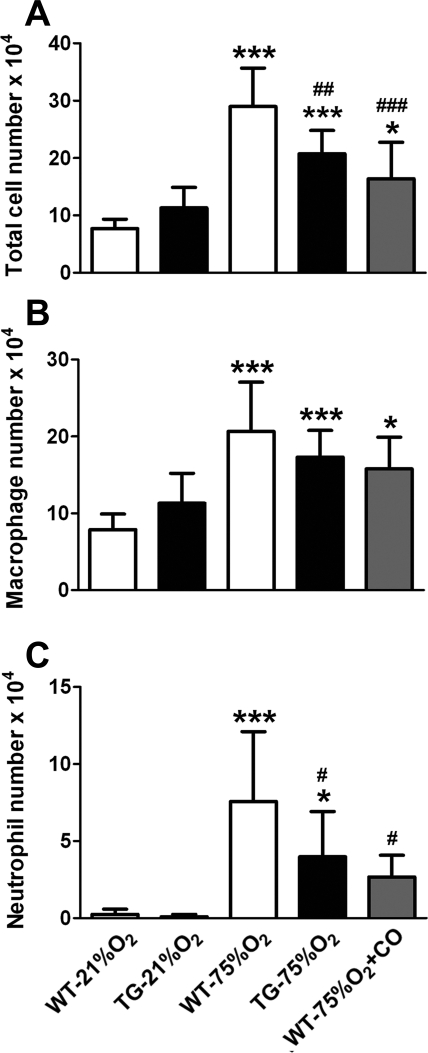
Fig. 2.
Hyperoxia-induced inflammatory cell influx in neonatal mouse lungs is attenuated by HO-1 overexpression and carbon monoxide (CO) inhalation. Total (A) and differential cell counts (B and C) were performed in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid after 2 wk of exposure to room air (21% O2) or hyperoxia (75% O2) revealing a modest effect on the number of macrophages (B) and a significant decrease in the number of neutrophils (C) in hyperoxic HO-1 overexpressing mice and mice receiving inhaled CO, compared with WT controls (n = 10 mice per group). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 vs. WT-21% O2; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. WT-75% O2.