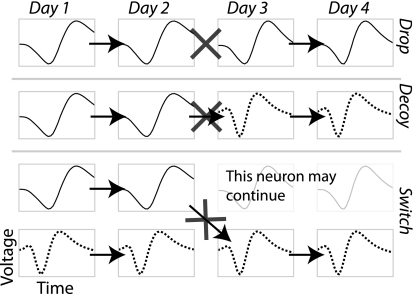
Fig. 4.
Types of errors we can make while trying to label the same neurons over multiple sessions. Drop errors occur when the target neuron continues but the classifier fails to positively identify it across one of the gaps (indicated by the X). The original label is then a false negative until the target neuron actually disappears. Decoy errors occur when the target neuron disappears at the same time as a new neuron appears and the classifier mistakenly labels the new neuron as being the same as the old one. The label is then a false positive until the new neuron disappears. Switch errors occur when a distracter neuron is present simultaneously with the target and the classifier mistakenly switches the label to the distracter. Switch errors are the least likely because they essentially require the classifier to simultaneously make a drop and a decoy error.