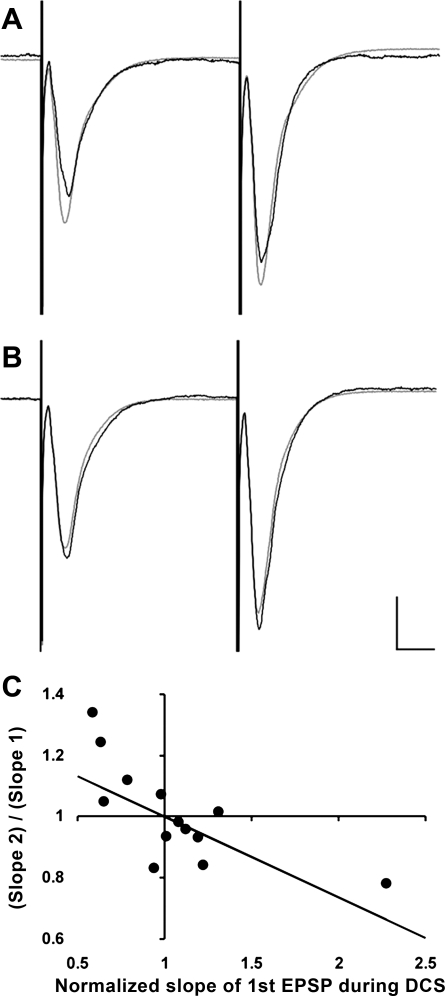
Fig. 4.
DCS has opposite effects on fEPSP facilitation and paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) in CA1 apical synapses in electrodes' configuration shown in Fig. 3C. A: typically, cathodal DCS inhibits first fEPSP and increases the PPF ratio. B: anodal DCS facilitates first fEPSP but reduces the PPF ratio. In both cases, fEPSPs are in gray color before DCS and in black during DCS. fEPSPs after DCS were similar to those before DCS, as shown in Fig. 2, and they were omitted for clarity. The scaling bars are 500 µV and 10 ms, respectively. C: scatter plot and the best fit of the relationship between the changes in normalized PPF ratios and in changes in normalized fEPSPs caused by −200, −100, +100, or +200 μA DCS. PPF ratios during DCS were normalized to PPF ratios before DCS. In the absence of DCS, both normalized PPF ratios and normalized fEPSPs were equal to 1. Linear fit of the relationship in 8 hippocampal slices reveals significant negative correlation with a slope of −0.26 ± 0.03 (P < 0.001), which is in agreement with a presynaptic effect of DCS.