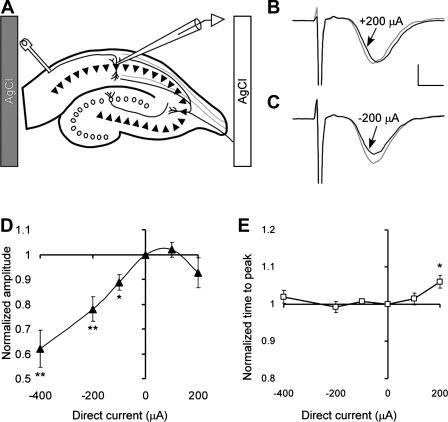
Fig. 7.
Effect of DCS on population spikes in CA1 neurons stimulated antidromically when DCS current is approximately parallel or antiparallel to AP propagation. A: positions of the electrodes. B andC: representative CA1 population spikes before (gray line) and during (black line) 200 μA of anodal and cathodal DCS, respectively. The scaling bars represent 1 mV and 1 ms, respectively. D: effect of DCS on normalized amplitude of the population spikes. Values of the spike amplitude are 62 ± 7, 78 ± 5, 89 ± 3, 102 ± 3, and 93 ± 6% for DCS of −400, −200, −100, +100, and +200 μA, respectively. One-way ANOVA demonstrate significant dependence spike amplitude on the DCS condition, F(4,23) = 8.8; P = 0.0002. Numbers of the slices per condition are 6, 6, 5, 6, and 5, respectively. E: effect of DCS on normalized time interval between the stimulus and the population spike. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.