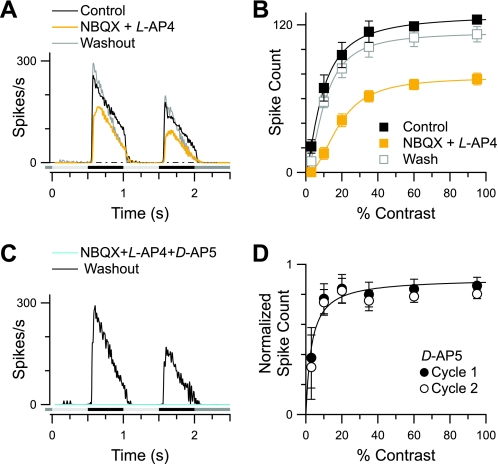
Fig. 2.
2,3-Dioxo-6-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo[f]quinoxaline-7-sulfonamide disodium salt (NBQX)-resistant inputs in OFF-BSGCs. A: average spike-time histograms at the highest stimulus intensity (95% contrast) show the NBQX and L-(+)-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid (L-AP4)-resistant response (yellow trace). B: mean spike count vs. stimulus contrast is reduced significantly but not blocked by 50 μM NBQX and 50 μM L-AP4 (n = 6). C: the addition of D-(−)-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (D-AP5) in the presence of NBQX and L-AP4 reversibly eliminated all spiking (cyan trace). D: mean spike count in the presence of D-AP5 alone, normalized to control. D-AP5 suppressed spiking most strongly at the lowest contrast (3%; n = 5).