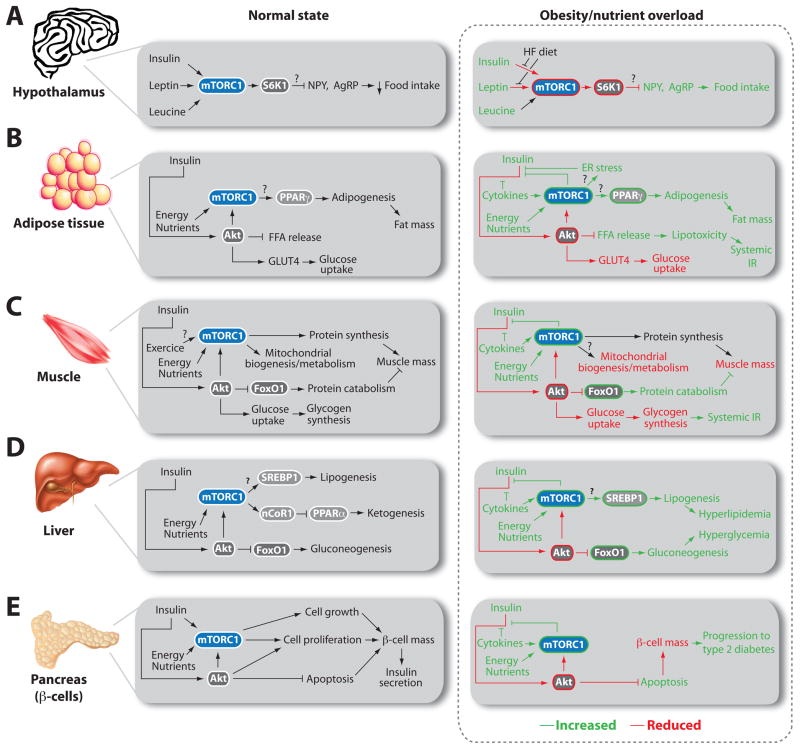
Figure 4. mTOR signaling and metabolism.
The roles of mTOR signaling in the regulation of tissue metabolism in the normal (left side) or obese/nutrient overload state (right side).
(A) In the hypothalamus, mTORC1 activation reduces the expression of orexigenic peptides (NPY, AgRP) through an unclear mechanism that involves S6K1. High fat diets reduce the ability of leptin and insulin to promote mTORC1 activity and reduce food intake.
(B) In adipose tissue, mTORC1 activation promotes adipogenesis by activating PPAR-γ. mTORC2-Akt activation reduces lipolysis and promote glucose uptake. High circulating nutrients and cytokines promote mTORC1 activity in obesity, which inhibits insulin signaling and cause insuline resistance (IR) through various mechanisms.
(C) In muscles, mTORC1 play crucial role in regulating protein synthesis, mitochondrial biogenesis, and oxidative metabolism. Muscle contractions increase mTORC1 activity. mTORC2-Akt activation induces glucose uptake and blocks protein catabolism. Similar to adipose tissue, the elevation of mTORC1 activity by obesity/nutrient overload blocks insulin signaling. The reduction in mTORC2-Akt action promotes protein catabolism and reduces glucose uptake, contributing to muscle mass loss and systemic IR.
(D) In the liver, mTORC1 activation reduces ketone body production by inhibiting PPAR-α activity. mTORC1 also promotes hepatic lipogenesis by activating SREBP1. Alternatively, mTORC2-Akt blocks FoxO1 activity and the activation of gluconeogenesis. Liver mTORC1 activity is elevated in obesity/overfeeding, which promotes hepatic IR, unrestrained gluconeogenesis, and hyperglycemia.
(E) In the pancreas, mTORC1 regulates β-cell mass by promoting β-cell growth and proliferation. mTORC1 is also important for insulin production/secretion. The mTORC2-Akt axis positively affects β-cell mass by promoting proliferation and survival. Obesity/nutrient overload drives mTORC1 activity in β-cells. Sustained activation of mTORC1 ultimately cause β-cell apoptosis by inhibiting Akt signaling. The loss of β-cells favors progression towards diabetes.