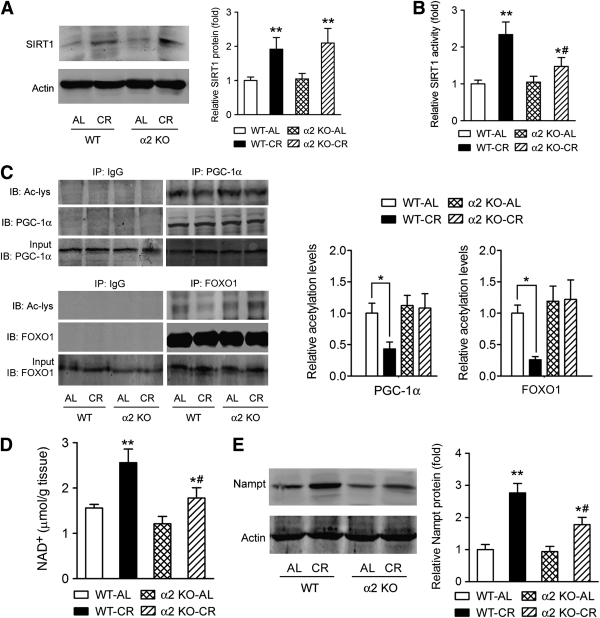
FIG. 5.
Loss of AMPK-α2 compromises the CR-induced activation of Nampt-SIRT1 axis. A: The increase of SIRT1 protein expression by CR in muscle was not affected by loss of AMPK-α2. B: SIRT1 was enriched by immunoprecipitation and then subjected to an acetylation activity assay to determine the SIRT1 activity. The increase of SIRT1 activity in muscle of CR mice was blunted by deletion of AMPK-α2. C: PGC-1α and FOXO1 were immunoprecipitated and probed with anti–acetyl-Lys (Ac-Lys) to assess the acetylation of PGC-1α and FOXO1, which reflect the deacetylation ability of SIRT1. CR increased deacetylation of PGC-1α and FOXO1 in skeletal muscle in WT mice but not in AMPK-α2−/− mice. D: Effects of CR on the NAD+ level in skeletal muscle were suppressed in AMPK-α2−/− mice. E: The upregulation of Nampt protein by CR was attenuated by deletion of AMPK-α2. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. AL; #P < 0.05 vs. WT. n = 6 per group. α2 KO, AMPK-α2 knockout mice; IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblot.