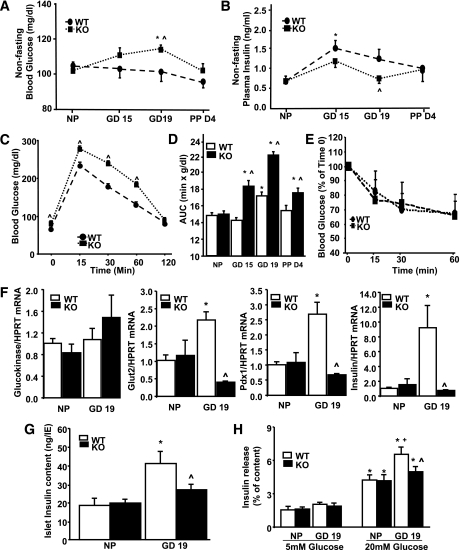
FIG. 6.
Glucose homeostasis in pregnant PancMet KO mice. Pregnant PancMet KO mice displayed significantly increased blood glucose (A) and significantly decreased plasma insulin (B) at GD19. Results are means ± SEM and were obtained from pregnant, PPD4, and nonpregnant (NP) wild-type (WT) (n = 4–8) and PancMet KO (n = 4–7) mice. *P < 0.05 vs. nonpregnant mice of their corresponding genotype; ^P < 0.05 vs. wild type at the same GD. C: Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test in wild-type (n = 7) and PancMet KO (n = 6) mice at GD19. Results are means ± SEM. ^P < 0.05 vs. wild type at the same time point. D: Area under the curve (AUC) calculated from the intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test experiments in which nonpregnant and pregnant wild-type (n = 5–7) and PancMet KO (n = 6–8) mice at GD15 and -19 and PPD4 were examined. Results are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 vs. nonpregnant mice of their corresponding genotype; ^P < 0.05 vs. wild type at the same GD or PP day. E: Insulin tolerance test in pregnant wild-type (n = 5) and PancMet KO (n = 6) mice at GD18. Both types of mice show similar response to insulin administration. F: Real-time PCR analysis of glucokinase, GLUT2, Pdx-1, and insulin mRNA expression in total islet RNA from islets isolated from nonpregnant and pregnant (GD19) wild-type (n = 5–6) and PancMet KO (n = 3–5) mice. Results are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 vs. wild-type nonpregnant; ^P < 0.05 vs. wild-type GD19. HPRT, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. G: Insulin content in islets isolated from nonpregnant and pregnant (GD19) wild-type (n = 6) and PancMet KO (n = 6) mice. Results are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 vs. wild-type nonpregnant; ^P < 0.05 vs. wild-type GD19. H: GSIS was performed in groups of 10 islets of similar sizes obtained from nonpregnant and pregnant (GD19) wild-type (n = 5) and PancMet KO (n = 5) mice and incubated for 30 min with 5 or 20 mmol/L glucose. Results are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 vs. 5 mmol/L glucose of their corresponding genotype; +P < 0.05 vs. nonpregnant wild type at 20 mmol/L glucose; and ^P < 0.05 vs. wild-type GD19 at 20 mmol/L glucose.