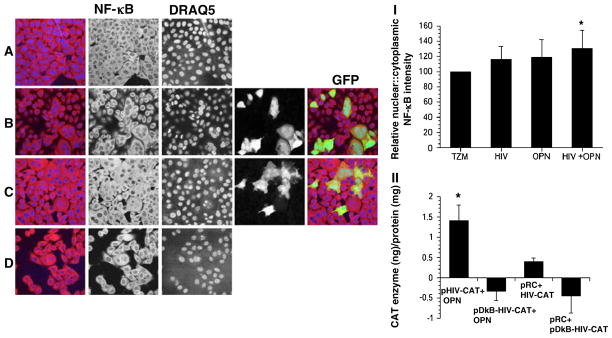
Fig. 3.
NF-κB activity is increased in HIV-infected cells expressing OPN. TZM-bl cells infected with HIVR3Nef+GFP were fixed and immunostained for NFκB (red) and nuclei with DRAQ5 (blue). a TZM-bl cells only; b HIV-infected TZM-bl; c HIV-infected TZM-bl expressing OPN; d TZM-bl infected with Ad-OPN; (I) the relative normalized nuclear:cytoplasmic intensity of NFκB is shown. All pictures were taken on a LSM510 Meta at the same pinhole and intensity settings. (II) TZM-bl cells were co-transfected with HIV-LTR-CAT reporter constructs encoding an intact (pHIV-CAT) or mutated NFκB (pDkB-HIV-CAT) binding domain and control (pRC) or OPN-expressing plasmid (OPN). CAT protein was measured by ELISA. The means and standard deviations of a representative of two independent experiments are shown