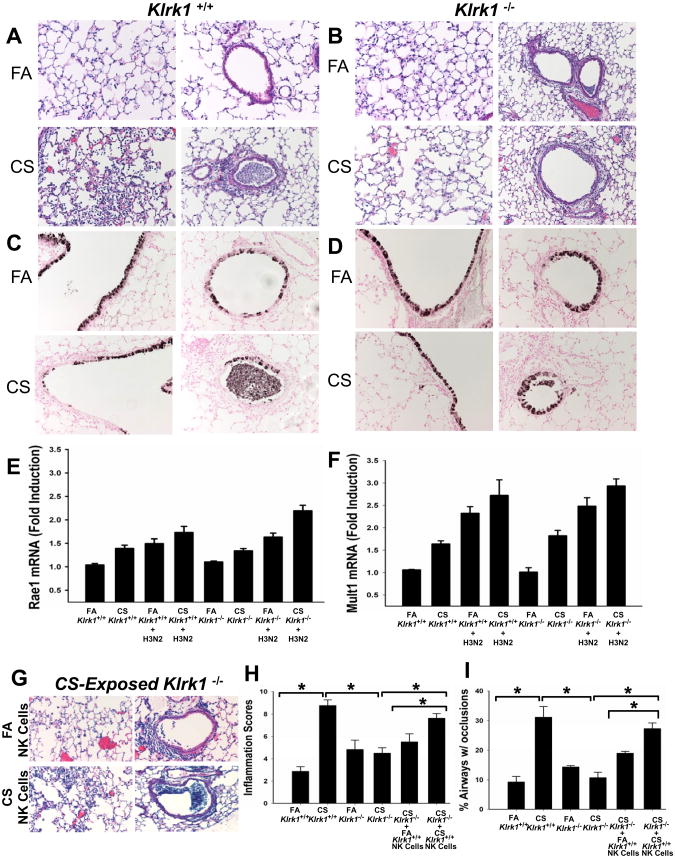
Figure 5. CS-exposed Klrk1-/- mice lack enhanced cellular responses associated with influenza infection.
Mice were infected with 2 × 103 pfu influenza virus and endpoints were measured 4 days after infection. (A-B) H&E stained lung sections representing changes in lung inflammation and airways obstruction between groups. (C-D) Clara cell secretory protein (CCSP) immunohistochemistry staining of lung sections showing epithelial damage of large airways and small airways. (E-F) Total RNA was isolated from lung homogenates of FA- or CS-exposed Klrk1+/+ and Klrk1-/- mice with and without influenza infection. Raet1 and Mult1 transcripts were assayed by quantitative RT-PCR and normalized to Rpl32. (G) H&E stained lung sections of influenza-infected CS-exposed Klrk1-/- mice which received NK cells from FA or CS-exposed Klrk1+/+ mice. (H) Semi-quantitative assessment of inflammation severity and distribution. (I) Quantitation of the percentage of intrapulmonary airways exhibiting any degree of airways obstruction. (n = 4-8 mice per group)