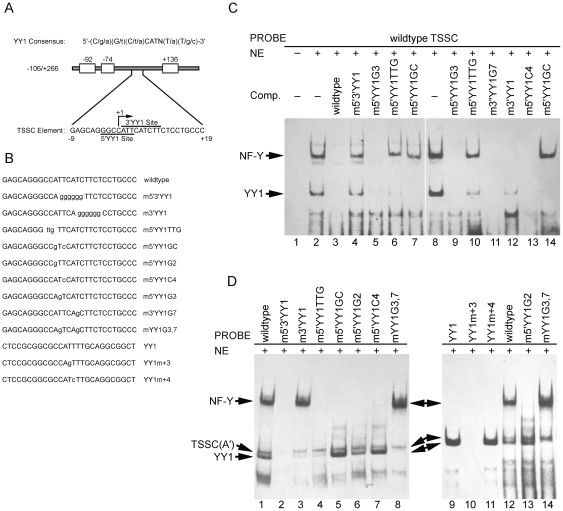
Figure 2. Characterization of the TSSC element of the exon 1a promoter.
(A) The consensus sequence for YY1 binding is shown, where the upper case letters represent the preferred bases. The YY1 binding site contains a conserved core 5′-CAT-3′, which is essential for efficient binding, and is flanked on either side by variable regions. Two potential binding sites for YY1 were identified within the TSSC element and each putative binding site for YY1 is marked. (C) Competition gel shift assays were performed with HeLa nuclear extract to define the binding specificity of YY1 and NF-Y to the TSSC element. Each competitor used was added in a 200-fold molar excess. The applied competitors with mutations in the YY1 consensus site are described in (B) and Table 1 . (D) Ability of the TSSC mutant oligonucleotides to form YY1 or NF-Y complexes. Wild type TSSC and 5′ and/or 3′YY1 mutant oligonucleotides were labeled and used in EMSAs with HeLa nuclear extract. Note: TSSC(A′), unidentified binding complex.