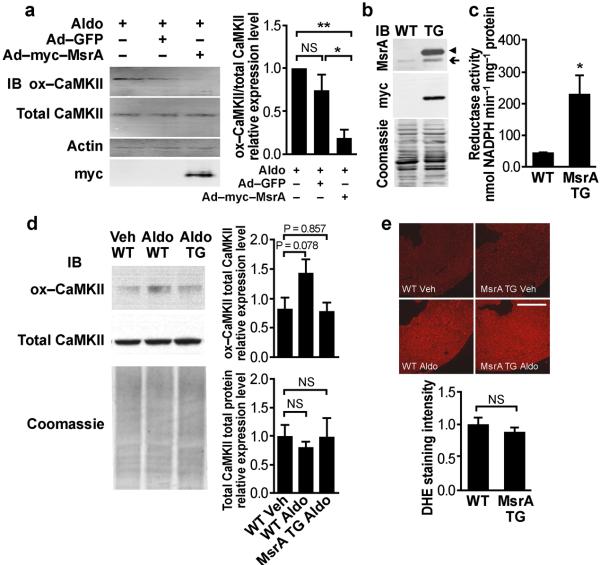
Figure 2.
Transgenic (TG) myocardial MsrA over-expression reduces CaMKII oxidation. (a) Representative immunoblot of CaMKII oxidation in neonatal myocytes. CaMKII oxidation is reduced by pre-infection with an adenoviral construct over-expressing myc tagged human MsrA. Summary data for n = 3 trials, P = 0.008, One-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Bonferroni's multiple comparison test versus Aldo-treated, non-infected control. (b) Representative immunoblot shows over-expression of MsrA in hearts from transgenic mice. The myc tagged human MsrA transgene (◀) runs higher than endogenous MsrA (←). (c) Cardiac MsrA activity is increased in transgenic mice compared to WT littermates. *P = 0.035, Student's t-test, n ≥ 3 mice per genotype. (d) WT mice infused with Aldo (1.44 mg kg−1 d−1, 2 weeks) show a substantial trend towards increased CaMKII oxidation by Western blotting in total heart homogenates, P = 0.078. MsrA transgenic mice appear resistant to Aldo-induced CaMKII oxidation. Total cardiac CaMKII expression levels remain similar between MsrA transgenic mice and WT control littermates, n = 6 mice per genotype. (e) DHE fluorescence of viable, cryopreserved myocardium after 15 minutes Aldo (10−7 mol L−1) stimulation. Aldo increases DHE fluorescence similarly in MsrA transgenic and WT hearts. Scale bar = 1 mm. n ≥ 3 mice per genotype.