Abstract
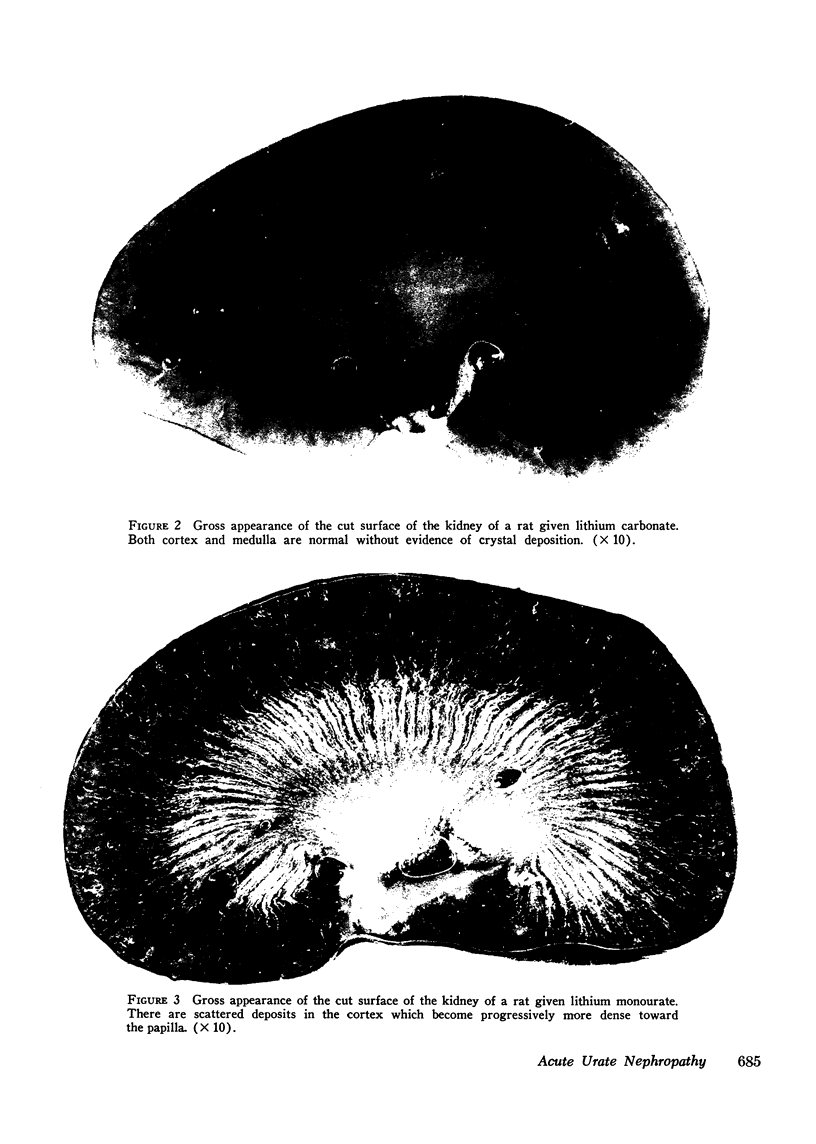
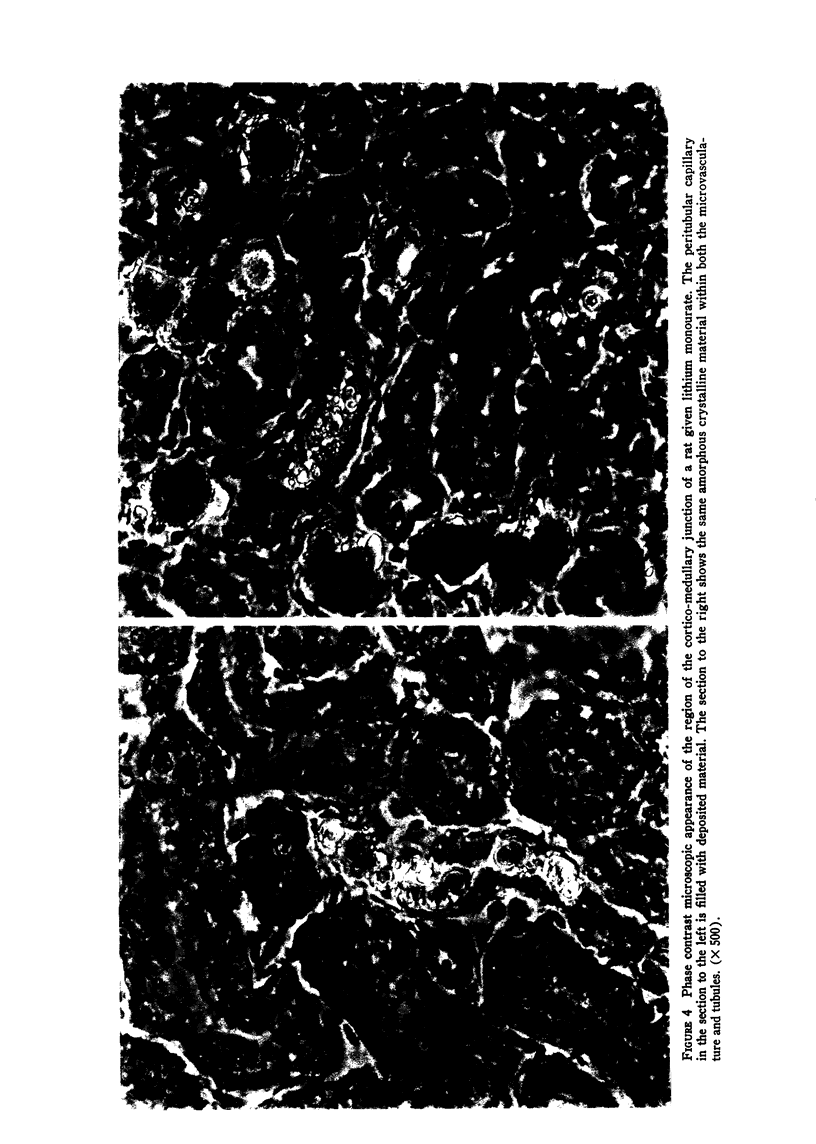
The early pathophysiological changes in acute urate nephropathy were investigated in a rat model using micropuncture, clearance, and morphologic methods. Plasma urate was increased from 1.2 +/- 0.6 to 20.1 +/- 3.1 mg/100 ml (P less than 0.001). Urinary urate rose from 24.3 +/- 5.1 to 142.2 +/- 21.0 mg/100 ml (P less than 0.001). Renal plasma flow and glomerular filtration rate fell to 17 and 14% of control values, respectively, and urine flow rate decreased from 11.3 +/- 4.8 to 4.2 +/- 2.2 mul/min (all P less than 0.005) Superficial nephron filtration rate fell less than that of the whole kidney (70 vs. 86%). Both proximal and distal tubular pressures were increased from 10.6 to 26.1 mm Hg and from 7.2 to 24.7 mm Hg, respectively (P less than 0.005). Efferent arteriolar and peritubular capillary pressures were increased twofold. Vascular resistance beyond the peritubular capillaries increased from 4.8 X 10(9) to 21.6 X 10(9) dynes s/cm5. Extensive deposits of uric acid and urate were found in the tubular system and vasa recti from the corticomedullary junction to the tip of the papilla. It is concluded from these experiments that not only tubular obstruction in the collecting ducts, but also obstruction of the distal renal vasculature, are the primary early pathogenetic events in acute urate nephropathy.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartoli E., Conger J. D., Earley L. E. Effect of intraluminal flow on proximal tubular reabsorption. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):843–849. doi: 10.1172/JCI107248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Konnen K. S., Tucker B. J. Glomerular filtration response to elevated ureteral pressure in both the hydropenic and the plasma-expanded rat. Circ Res. 1975 Dec;37(6):819–829. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.6.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COULOMBE J. J., FAVREAU L. A new simple semimicro method for colorimetric determination of urea. Clin Chem. 1963 Feb;9:102–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conger J. D., Burke T. J. Effects of anesthetic agents on autoregulation of renal hemodynamics in the rat and dog. Am J Physiol. 1976 Mar;230(3):652–657. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.3.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conger J. D., Rhoads H. N., Christie S. N., Burke T. J. A modification of the fluorescence method for micro-inulin determinations. Kidney Int. 1975 Nov;8(5):334–337. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M., Singer I. Lithium and water metabolism. Am J Med. 1975 Aug;59(2):153–157. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREI E., 3rd, BENTZEL C. J., RIESELBACH R., BLOCK J. B. RENAL COMPLICATIONS OF NEOPLASTIC DISEASE. J Chronic Dis. 1963 Jul;16:757–776. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(63)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest J. N., Jr, Cohen A. D., Torretti J., Himmelhoch J. M., Epstein F. H. On the mechanism of lithium-induced diabetes insipidus in man and the rat. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1115–1123. doi: 10.1172/JCI107649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa S. P. Acute renal railure in association with hyperuricemia: its recovery with ethacrynic acid. South Med J. 1971 Jun;64(6):676–678. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197106000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. H., Kurtz T. W., Preuss H. G., Weller J. M. Measurement of renal blood flow in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jun;149(2):470–472. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. J., Stavric B., Chartrand A. Uricase inhibition in the rat by s-triazines: an animal model for hyperuricemia and hyperuricosuria. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 May;131(1):8–12. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRITZLER R. A. Anuria complicating the treatment of leukemia. Am J Med. 1958 Oct;25(4):532–538. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellstrand C. M., Cambell D. C., 2nd, von Hartitzsch B., Buselmeier T. J. Hyperuricemic acute renal failure. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Mar;133(3):349–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinenberg J. R., Bluestone R., Schlosstein L., Waisman J., Whitehouse M. W. Urate deposition disease. How is it regulated and how can it be modified? Ann Intern Med. 1973 Jan;78(1):99–111. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-78-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakoff I. H. Use of allopurinol in preventing hyperuricemia in leukemia and lymphoma. Cancer. 1966 Nov;19(11):1489–1496. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196611)19:11<1489::aid-cncr2820191105>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. J., Martin C. M. Effects of diuretic states on collecting duct fluid flow resistance in the hamster kidney. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jul;229(1):13–17. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez G. O., Oster J. R., Vaamonde C. A. Incomplete syndrome of renal tubular acidosis induced by lithium carbonate. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Sep;86(3):386–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIESELBACH R. E., BENTZEL C. J., COTLOVE E., FREI E., 3rd, FREIREICH E. J. URIC ACID EXCRETION AND RENAL FUNCTION IN THE ACUTE HYPERURICEMIA OF LEUKEMIA. PATHOGENESIS AND THERAPY OF URIC ACID NEPHROPATHY. Am J Med. 1964 Dec;37:872–883. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector F. C., Jr, Brunner F. P., Seldin D. W. Mechanism of glomerulotubular balance. I. Effect of aortic constriction and elevated ureteropelvic pressure on glomerular filtration rate, fractional reabsorption, transit time, and tubular size in the proximal tubule of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):590–602. doi: 10.1172/JCI105373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. F., CHEN Y. C. Experimental uric acid nephritis in the rabbit. J Exp Med. 1957 Jun 1;105(6):615–622. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.6.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegmiller J. E., Frazier P. D. Biochemical considerations of the renal damage of gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 1966 Nov;25(6 Suppl):668–672. doi: 10.1136/ard.25.suppl_6.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegmiller J. E. The acute attack of gouty arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1965 Oct;8(5):714–725. doi: 10.1002/art.1780080431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I., Rotenberg D., Puschett J. B. Lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: in vivo and in vitro studies. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1081–1091. doi: 10.1172/JCI106900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavric B., Johnson W. J., Grice H. C. Uric acid nephropathy: an experimental model. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Feb;130(2):512–516. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S. M., Galen M. A., Lazarus J. M., Lowrie E. G., Hampers C. L., Jaffe N. Hemodialysis for acute anuric uric acid nephropathy. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Aug;129(8):956–958. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120450062014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINTRAUB L. R., PENNER J. A., MEYERS M. C. ACUTE URIC ACID NEPHROPATHY IN LEUKEMIA. REPORT OF A CASE TREATED WITH PERITONEAL DIALYSIS. Arch Intern Med. 1964 Jan;113:111–114. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1964.00280070113018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman J., Bluestone R., Klinenberg J. R. A preliminary report of nephropathy in hyperuricemic rats. Lab Invest. 1974 Jun;30(6):716–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman J., Mwasi L. M., Bluestone R., Klinenberg J. R. Acute hyperuricemic nephropathy in rats. An electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1975 Nov;81(2):367–378. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R. W., Watkins P. J., Matthias J. Q., Gibbs D. A. Allopurinal and acute uric acid nephropathy. Br Med J. 1966 Jan 22;1(5481):205–208. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5481.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]