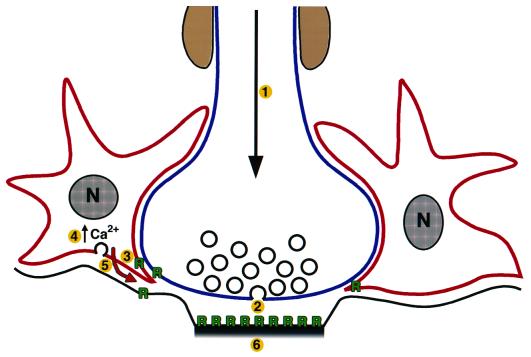
Figure 1.
Schematic of astrocyte–neuron intercellular signaling. Action potential firing in the neuron (1) induces neurotransmitter release from the presynaptic terminal (2), receptor activation on adjacent astrocytes (3), increases in intracellular Ca2+ (4), Ca2+-dependent neurotransmitter release from the astrocytes (5), and the activation of neighboring neurons and potentiation of interneuronal synaptic transmission (6). In addition, astrocyte-derived soluble neurotrophic factors (red arrow) are also likely to effect CNS synapse function. R, neurotransmitter receptor.