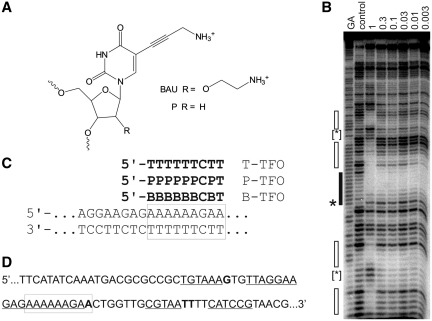
Figure 1.
(A) Chemical structures of bis-amino-U and propargylamino-dU. (B) DNase I footprint showing the interaction of B-TFO with the tyrT(43-59) fragment. The experiment was performed in 50 mM sodium acetate pH 5.0; TFO concentrations (µM) are shown at the top of each gel lane. The DNA was labelled at the 3′-end; the gel therefore runs 5′–3′ from top to bottom. The lane labelled control shows digestion of the DNA in the absence of oligonucleotide; GA is a marker specific for purines. The exact target site is shown by the filled box and the accompanying enhancement is indicated by an asterisks. Secondary binding sites are shown by the unfilled boxes and the enhancements are indicated by bracketed asterisks. (C) Sequence of the oligopurine tract in tyrT(43–59) and its interaction with the modified TFOs. The exact target site is boxed. (D) Sequence of a part of the tyrT(43–59) fragment showing the position of the secondary binding sites, which are underlined and the enhancements, which are shown in bold. The exact target site is boxed.