Figure 6.
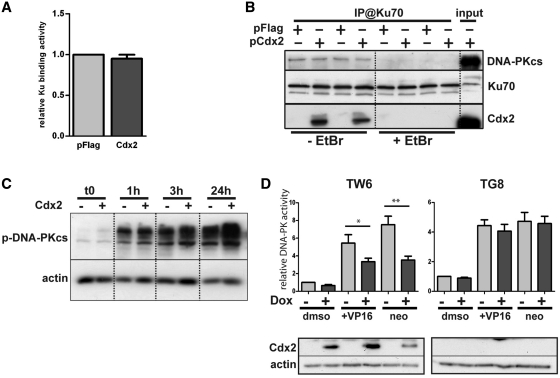
Cdx2 does alter neither Ku proteins and DNA-PKcs recruitment nor DNA-PK autophosphorylation but inhibits DNA-PKcs activity. (A) Cdx2 does not interfere with DSB Ku70 binding. HCT116 cells were transfected with pFlag (light gray) or Cdx2 (dark gray) expressing plasmid and Ku70 binding activity was assessed. Results represent the mean of at least four independent experiments. pFlag values were set at 1. (B) Cdx2 does not alter DNA-PKcs recruitment. HCT116 were transfected with either pFlag or pFlag-Cdx2 as indicated and immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-Ku70 antibodies in the presence or absence of Ethidium Bromide (EtBr) as indicated at the bottom of the figure. DNA-PKcs, Ku70 or Cdx2 were revealed by western blot. Twenty micrograms of whole-protein extract were loaded on the right line (input). (C) Cdx2 does not modify DNA-PKcs autophosphorylation. Time course analysis of the phosphorylation of the DNA-PKcs after etoposide treatment 100 μM for 1 hour of HCT116 cells transfected with pFlag or pFlag-Cdx2. Phospho-DNA-PKcs was revealed by western blot. β-actin was used to normalized the amount of loaded proteins. (D) Cdx2 inhibits DNA-PKcs activity. DNA-PKcs activity was assessed in HT29-TW6 or -TG8 (control) cells treated or not with etoposide (VP16) 100 μM or neocarzinostatin 200 ng/μL for 1 hour. Cdx2 expression was induced with doxycyclin when indicated (dark gray bars). Experiments without doxycyclin and etoposide treatment were considered as references and results were set at 1. Results illustrate the mean of at least six experiments and error bars represent SEM. Asterisk indicates a significant difference (**P < 0.01; *P < 0.05). Above, Cdx2 expression was checked by western blot using anti-Cdx2 antibody on 10 µg of whole-protein extracts. Actin was used as loading control.