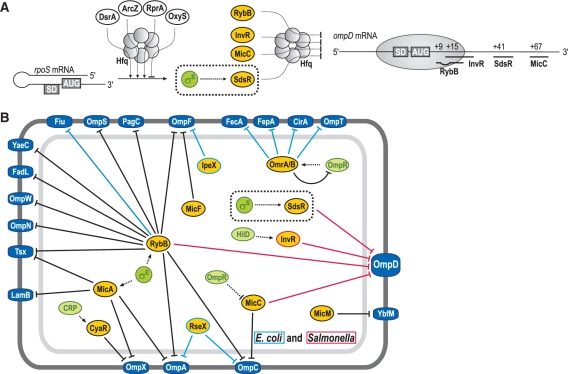
Figure 9.
(A) Schematic display of regulatory RNAs affecting rpoS and ompD expression post-transcriptionally. sRNA regulators controlling rpoS mRNA are depicted in white ellipses, those that regulate ompD mRNA expression are shown in yellow. Hfq is indicated as a circled hexamer, σS as a green circle. Positioning of the 30S ribosomal subunit and pairing-sites of RybB, InvR, SdsR and MicC sRNAs on the ompD CDS are shown on the right. (B) Network of Hfq-dependent sRNA regulating outer membrane protein synthesis in E. coli and Salmonella. Transcriptional regulators are represented as green, sRNAs as yellow and OMPs as dark blue circles, respectively. Black lines mark sRNAs and regulatory functions common to both species while light blue or red lines denote sRNAs or regulation specific to E. coli or Salmonella, respectively. Note that a gene similar to ompD is generally present in E. coli and referred to as nmpC. However, in many E. coli strains including strain K12—our reference here—the NmpC/OmpD porin is not expressed due to an insertion element (84,85); consequently we indicate sRNA-mediated regulation of OmpD as specific to Salmonella, although the nmpC mRNA was also shown to be a RybB target in E. coli (24).