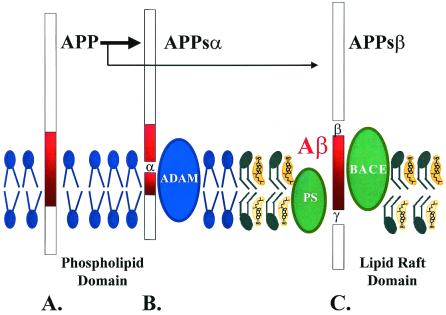
Figure 1.
A putative model of the processing of APP in relation to the lipid composition of membranes. (A) APP is a transmembrane protein. (B) Cleavage of APP by α secretases, such as ADAM10, produces APPsα, which requires a membrane domain that is cholesterol poor, such as phospholipid domains. (C) Cleavage of APP by the β and γ secretases, BACE, and Presenilin (PS) produces Aβ and APPsβ. This step requires a membrane domain that is cholesterol rich, such as a lipid raft. APP processing can be directed toward α-secretase or β/γ-secretase pathways by modulating the cholesterol content of the membranes. Lipid identities: blue, phospholipid; green, sphingolipids; yellow, cholesterol.