Figure 5.
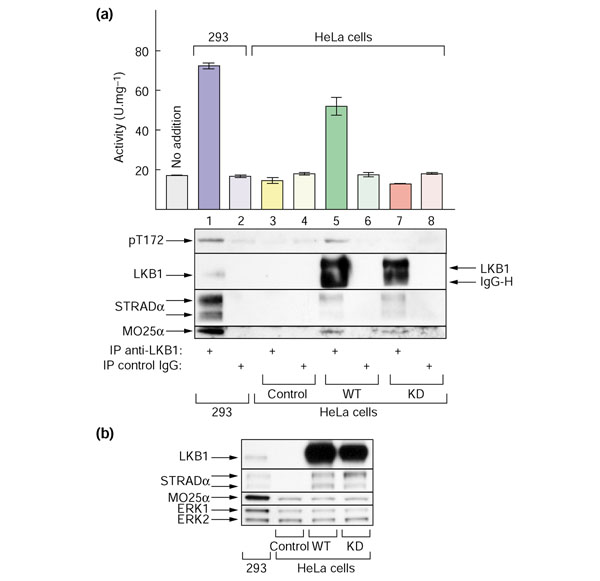
Endogenous AMPKK activity (that is, ability to activate AMPKα1 catalytic domain) can be immunoprecipitated from 293 cells using anti-LKB1 antibody, but activity can only be immunoprecipitated from HeLa cells if they stably express wild-type LKB1, but not a catalytically-inactive mutant. (a) LKB1 was immunoprecipitated from 0.5 mg cell extract derived from untransfected HEK-293T cells (lanes 1,2), untransfected HeLa cells (control; lanes 3,4), or HeLa cells stably expressing wild-type LKB1 (WT; lanes 5,6) or a kinase-dead LKB1 mutant (D194A; KD, lanes 7,8). Immunoprecipitation used anti-LKB1 (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7) or a pre-immune control immunoglobulin (IgG; lanes 2, 4, 6, 8). Samples of each immunoprecipitate were used to assay activation of GST-AMPKα1 catalytic domain, to analyze phosphorylation of GST-AMPKα1 catalytic domain on Thr172 (middle panel), and to determine by western blotting the recovery of LKB1 and its accessory subunits (bottom panels). In lanes 5 and 7 some immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgG-H) had eluted from the protein G-Sepharose despite the fact that it had been cross-linked: this explains why LKB1 may not appear to comigrate in lanes 1, 5 and 7. Also shown at left in the top panel is the basal activity obtained when the GST-AMPKα1-catalytic domain was incubated with MgATP on its own (no addition). (b) Whole cell lysates from the same cells were analyzed by SDS gel electrophoresis and blots probed using anti-LKB1, anti-STRADα, and anti-MO25α antibodies. They were also probed with anti-ERK1/2 antibodies as loading controls.
