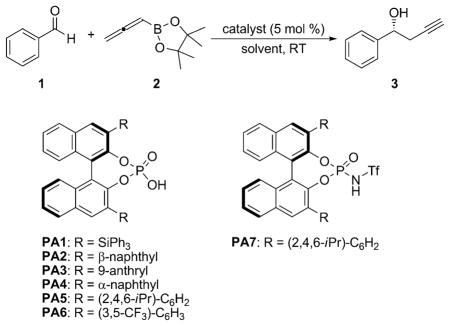
Table 1.
Catalyst screening and optimization for the propargylation of benzaldehyde.[a]
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Catalyst[b] | Solvent | t [h] | Yield [%][c] | ee [%][d] |
| 1 | PA1 | toluene | 40 | 94 | 0 |
| 2 | PA2 | toluene | 40 | 93 | 7 |
| 3 | PA3 | toluene | 40 | 92 | 20 |
| 4 | PA4 | toluene | 40 | 95 | 9 |
| 5 | PA5 | toluene | 40 | 91 | 74 |
| 6 | PA6 | toluene | 40 | 93 | 4 |
| 7 | PA7 | toluene | 40 | 94 | 16 |
| 8 | PA5 | benzene | 40 | 89 | 62 |
| 9 | PA5 | DCM | 40 | 87 | 43 |
| 10 | PA5 | PhCF3 | 40 | 94 | 68 |
| 11 | PA5 | p-xylene[e] | 40 | 92 | 75 |
| 12 | PA5 | toluene[e] | 40 | 92 | 77 |
| 13 | PA5 | toluene[e],[f] | 24 | 93 | 87 |
| 14 | PA5 | toluene[e],[f],[g] | 64 | 96 | 90 |
| 15 | PA5 | toluene[e],[f],[h] | 72 | 94 | 91 |
Reaction conditions: 1 (0.10 mmol), 2 (0.12 mmol), catalyst (5 mol%), unless otherwise specified.
All catalysts were washed with 6M HCl after purification by column chromatography.
Yields of isolated product.
Determined by chiral HPLC analysis.
Reaction conducted in presence of 4Å M.S.
20 Mol% catalyst used.
Reaction conducted at 0°C.
Reaction conducted at −20°C.
